Altair HyperMesh 2019 Release Notes
General
New Features
- Append entity attributes to Model Browser
- Append the entity attributes associated with components, properties, and materials to the browser as column data to facilitate fast and efficient review, editing, sorting, and filtering. Columns can be reorganized by dragging them to the desired position.
- Assembly view in Model Browser
- Quickly view an isolated list of all the assemblies in your model using the new Assembly view in the Model Browser.
- Metadata in Entity Editor
- A new section has been added to the Entity Editor to allow for easy review and editing of metadata. This is available for all entity types, and is also supported for appending as column data in relevant browser views.
Enhancements
- Duplicate extended entity selection for components
- Maintain associativity between elements and geometry using the "Duplicate" selection method added to the extended entity selection menu in the Reflect, Translate, and Rotate panels.
- 2D plotel elements supported by Mask Browser
- The Mask Browser now supports Plotel3 and Plotel4 elements.
- Maintain entity name when duplicating entities
- The original name assigned to an entity is retained when creating new entities using the "Duplicate" option in the Model Browser.
- Select IDs in browser spinbox
- Select entity IDs from the spin box located in the top corner of the browser.
- Entity management in Include files
- Newly created entities are automatically organized into the Include file of their current collector.
- ID Manager enhancements
- Entities are listed by ID pools per Include file or the Master Model. Duplicate IDs are permitted when renumbering a model for certain entities when "Allow Duplicate IDs on Correction" is selected. CSV export captures min and max IDs and per include entity counts, while import prompts you if your model contains overlapping ID ranges.
- Undefined entities support for components
- Undefined entities now support components.Note: Components are not created for undefined connectors.
Resolved Issues
- The From overflow column in the ID Overflow List dialog shows incorrect IDs for overflow entities.
- Closing the ID Manager dialog while a push panel was active results in a crash.
- When an entity name is the same as another entity’s ID, you cannot change its ID and color. This is valid for all entity types listed in the Model Browser.
- Adjusting orientation using the Orientation Review tool deletes elements.
- Updating pressure direction changes the magnitude of pressure.
- Saving and reopening HyperMesh models that contain weld data causes segmentation errors.
- Face selection issues.
- Displaying load magnitudes, inconsistently shows both fixed and scientific formats.
- Moving the application from one monitor to another occasionally fails to show the panel area correctly.
- The "Export All Self Contained" selection option, accessed from the Include view context menu does not use the updated command.
- Elements are organized incorrectly when you set Destination Component to "Original Collector" in the Transformation dialog.
- Using the Shift+Tab keyboard shortcut in a panel moves the selection outside of the panel on Linux.
- The Reflect panel assigns nodal thickness to incorrect nodes.
- Character limitation while typing in an input field of a panel.
Graphics
New Features
- 2160p Ultra High Definition support
- 2160p Ultra High definition is supported in HyperWorks products with proper DPI scaling and sharper graphics area.
- Freetype fonts supported in graphics area and HyperMesh panels
- Freetype fonts have been added and bundled for smoother anti-aliased fonts being rendered in the graphics areas within HyperWorks products and HyperMesh panels.
Enhancements
- Element Quality view
- Review your model's overall element quality categorized as Worst, Fail, Warn, Good and Ideal using the Quality Index Range (QI Range) legend that has been added to the Element Quality view.
- Improved graphics selection and performance improvements for displaying nodes in graphics
- The rendering of nodes that are being displayed has been accelerated with enhanced graphics rendering techniques.
Known Issues
- In certain cases, rotational framerates will be reduced while entity types
such as springs/gaps, element handles,loads, and so on are visible.Tip: Enabling the optimize view ctrls checkbox () may increase rotation framerates.
- If you are experiencing performance issues for animations, interactive meshing, and product stability, it is recommended that you use Windows NVIDIA drivers version 419.53 (or higher) for HyperWorks 2019 which introduces enhancements in these areas.
Resolved Issues
- Edge selection does not work while spherical clipping is on.
Connectors
New Features
- Undo-Redo connector support
- Undo/redo operations are supported by all connector related functionality.
- Connector Groups
- Connectors are now organized inside of the newly supported connector group entity, and not components.
- Connector support for configuration management
- Unrealized connectors can be made active/inactive based on their link state. If a connector's link is inactive, then the connector will automatically be made inactive. This functionality is supported for connectors with part links, component links, or property links.
- Second pass projection for RADIOSS welds
- Find exact contact points with the "Use 2nd projection" parameter. This parameter is supported for all realizations, where nodes are on a tria or quad face, as well as for all 1D element realizations, hexa element realizations (only if shell gap is used), and penta realizations (only if consider shell thickness and offset for solid positioning is off).
- Remove links from connectors
- Remove links from connectors in the Connector Browser, Component Link view with the "Remove From Connectors" right-click contextual menu option. You can choose to remove links from selected, displayed, or all connectors. Layers can be automatically updated once links have been removed with the "Update Layer" option in the Remove From Connectors Settings dialog.
- Enhanced display functionality for HAZ element
- Automatically update the display of HAZ elements associated with connectors and link entities that are being isolated, displayed, or hidden with the "Consider HAZ Elements" option in the Browser Configuration dialog.
- Reduce search/isolation to specific components and elements
- Specify a type of link and weld elements to isolate when you are reviewing a realization with the "Filter Links to" option in the Browser Configuration dialog. You can choose to isolate an entire link component, only the elements on which the projection falls, or the elements on which the projection falls along with the elements which connects connector FE.
- Get link information for resolved entities
- Get link information for resolved entities and organize this information per link index using the hm_ce_getresolvedlinkentities API. The output will show ‘entity-id’ if a link entity is present in the current model, otherwise it will show ‘0’.
- Unregister realized entities
- Unregister realized entities from connectors using the *CE_FE_UnregisterRealizedEntities API. Once you have successfully unregistered realized entities from a connector, the state of the connector is changed to Modified (blue). The realized entities that were unregistered from the connectors will not be deleted during connector “unrealization” and “deletion with FE”.
Enhancements
- Connector support for *entitysupressactive API
- The *entitysupressactive API now supports connector entities, and can be used to set connectors to an active/inactive state.
- Support for hexa thickness type during FE absorption of ACM connectors
- Define a hexa thickness type for ACM spot, seam, and adhesive absorption using the Hexa thickness type preference option.
- 16 hexa nugget added to nugget library
- A hexa pattern 16 hexa single sym has been added to library of nuggets.
- Manage redundant connectors
- During entity management, an ID check has been added to check for redundant connectors. If connector ID is selected along with keep both attributes, then redundant connectors will be imported and renumbered as needed. The former connector ID will be written to the comment field for each individual connector.
- Dynamic realization for connectors outside of components
- During connector realization for post scripts that do not create components, weld elements will be automatically organized in a newly created component.
- Connector browser Common Top view
- View a list of all the link entities (component links, property links, and part links) and connector group entities in your model with the Common Top view in the Connector browser.
- Color connectors by connector group
- Color connectors based on the connector group to which they belong using the Color by Connector Group visualization option.
- Seam weld support for multiple quad layers
- Specify a quad layer for all quad seam welds with the Coats parameter. This functionality allows the possibility to create more than one quad element layer in seam welds between the welded parts.
- hm_ce_checklinkentities API support parts
- The hm_ce_checklinkentities API now support parts.
Resolved Issues
- Issues with FE Absorb performance when called on small selection.
- When unloading parts attached to connectors, a segmentation error displays.
- Issues with 3D hole detection.
- Autopitch tool performance issues.
- Performance issues during FE absorption of hexa seam connectors.
- Autopitch tool crashes when working with larger models.
- When exporting connectors to xMCF format, a segmentation error displays.
- Correction on the realization for cweld (GS GRIDID) when used on solid elements.
- Issues with the *CE_Cleanup API. API now works with rbe3-cbush-rbe3 connectors.
- Issues with CFAST FE absorption when the CFAST’s are incomplete.
- Issues with element highlight in modeling window when working in Area Connector panel.
- Horizontal weld length is more than the calculated value for seam-quad LTB connector.
- Issues with bolt realization when the "skip imprint" option is used in Seam Connector panel.
- Issue with connector realization when RBE3 weight factor is greater than zero.
- Issue with connector export/import behavior when link names have ampersand (&).
Geometry
New Features
- Geometry faceting
- By default, geometry facets are saved to the .hm file, which improves the time to begin working when loading .hm files containing geometry. For pre-2019 .hm files, facets are immediately generated during file load. Optimized data storage to minimize .hm file size increase.
Enhancements
- Query 1D elements and their corresponding nodes
- Query 1D elements and their corresponding nodes from associated surface edges using the "by geom" advanced selection method.
Resolved Issues
- Miscellaneous issues related to robustness and performance.
2D Meshing
New Features
- Fix intersections and sliver elements
- The Boundary Shell Checker tool now allows you to automatically fix intersections and sliver elements in shell mesh. You can also automatically fix thousands of elements with high aspect ratio, smaller height, and intersections in a few seconds, which otherwise would take hours to fix manually.
Enhancements
- Mesh fusing
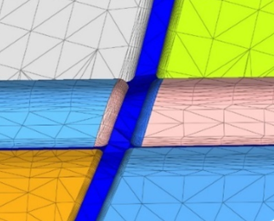
- Fusing technology is enhanced to automate external aerodynamic modeling process.
- BatchMeshing
-
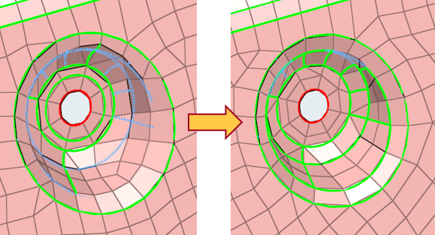
- Enhanced and simplified geometry cleanup
- Geometry cleanup has been enhanced to provide flexibility, consistency, and better feature capture.
- New and powerful mesh flow algorithm
- The new mesh flow algorithm considers the shape of the
geometry and aligns the mesh to create orthogonal meshes,
reduces the number and strategic placement of trias, and
controls the average element size to provide a more uniform
mesh.
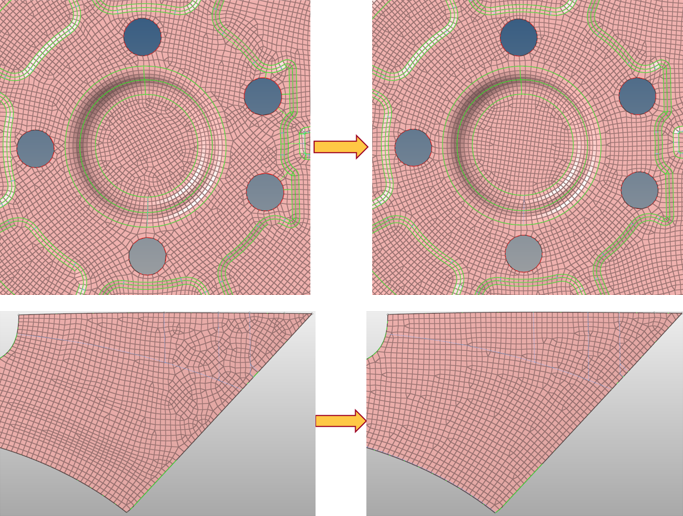
Figure 4. - Improved parameter GUI highlight the changes
- Bead, Logo and Thread recognition sections have been added to provide ease of use and better understanding of parameters based on feature.
- Define CAD import options in Batchmesher
- Defining CAD import options in Batchmesher overwrites those coming from the .ini files or the default values, and applies to all CAD files being imported. This enhancement allows options to be locally defined without having to modify the .ini files.
- Generate direct midmesh
- Generate a direct midmesh using Batchmesher. All options from the Midmesh panel are available supported.
- Midmesh
-
- Drive resulting mesh with target and minimum element size
- Drive the resulting midmesh using the target and minimum element size from the criteria file to enable the extraction size to be given independent of the edge/feature cleanup sizes. This also helps to eliminate unnecessary manual cleanup steps downstream.
- Performance improvements
- Performance improvements of up to 40% for midmesh creation.
- Enhancements to the Edit Edge and Edit Face tools
- Delete the 1D input loop and keep only free and non-manifold edges with the "Delete 1Ds" option in the Fill Face tool. Optionally keep boundary nodes locked to prevent disruption of neighboring faces with the Align Faces tool. Imprint a new geometry edge onto the midmesh with the "By geom edge" option. Considered gaps/cracks along with intersections with the "Detect intersections/gaps" option.
- General improvements
- Flattening option robustness.
- Rebuild mesh
- Rebuild mesh now supports shell elements associated with geometry to allow remeshing results coming from Batchmesher, for example, to correct local problem areas while still maintaining quality and flow.
- Map midmesh thickness
- Linear interpolation support was added for nodal thicknesses.
- Automatic refinement (HyperWorks X only)
- Automatically refine 1D and 2D elements with quad element transition
patterns using the brand-new Automatic refinement algorithm. This
algorithm is useful for refining around hot spot locations, and is
focused on aero and marine industry needs.
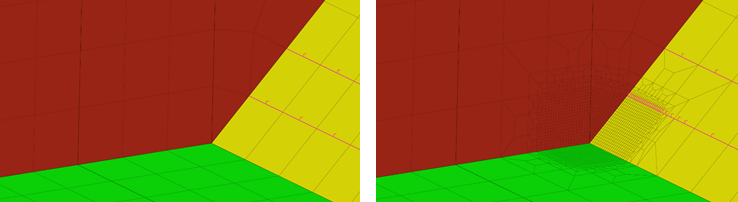
Figure 5. - Mesh coarsening
- Generate a new component containing the coarsened elements, and leave
the original component and its elements untouched with the "Retain input
mesh" option in the Coarsen Mesh tool. The coarsened elements will share
nodes with the original input mesh.
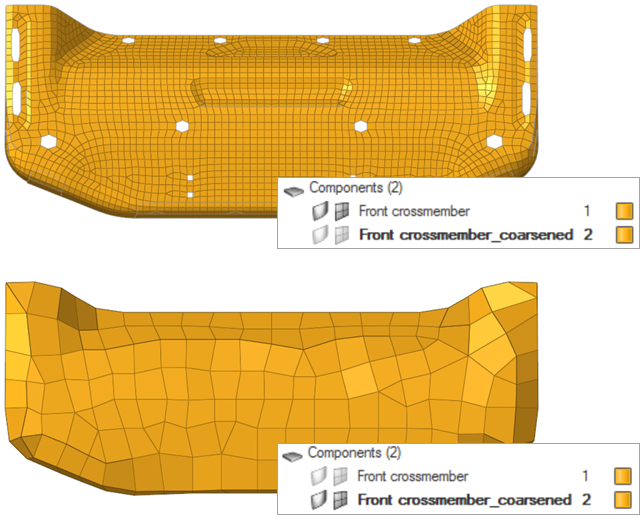
Figure 7. - Surface deviation
- Performance has been improved to make mesher competitive edge. Rouse of surface meshing for complex models has improved, and the number of meshing failures has significantly reduced. Mesh refinement performance and sizes has also improved.
- Adaptive tria remeshing
- Performance for large remesh models has been improved to significantly reduce the time it takes to remesh wrapped models. The robustness for mesher has also been improved to avoid free edges, intersections. Discrete topology input support and updates have also been added within meshing.
- Adaptive wrapper
- Wrap geometry directly using topological selection.
Resolved Issues
- Crashes and general instabilities with the Quality Index panel.
- Robustness issues for the Rigid Body mesher and Feature mesh controls.
- Issues with hole and gap filling for non-planar holes/gaps.
3D Meshing
New Features
- Tetrameshing method
- Lower memory utilization, enforce refinement, average and max-min size,
and create a smooth transition from surface using the new multi-threaded
meshing method added to the TetraMesher. This method also enables you to
control tetra growth from surfaces.
Model Elements Time (minutes) V 2017 V 2019 Headlamp model 6.4 mi 19 4 F1 car model 302 mi 367 146 - Tetramesh updates for geometry modification
- A new option has been added to update tetrahedral mesh on geometric operations. You can automatically update tetrahedral mesh associated with modified solid.
- Local tetrameshing controls
- Define tetra mesh controls for individual solids using local tetrameshing controls. You can define sizes or different meshing options for individual solids. During volume meshing, locally defined volume mesh settings will be enforced.
- Topology based volume meshing
- Volume Meshing mesh controls for tetrameshing can be defined for geometric solids or surfaces.
- Hex/Octree dominant meshing
- The Volume Meshing mesh control now supports Octree Dominant and Hex
Dominant core meshing options. You can define these options using the
"Core Mesh" attribute, accessed from the Mesh Controls Browser, Entity Editor. These options are integrated within
existing Volume Meshing controls setup, and can be used along with
boundary layers.
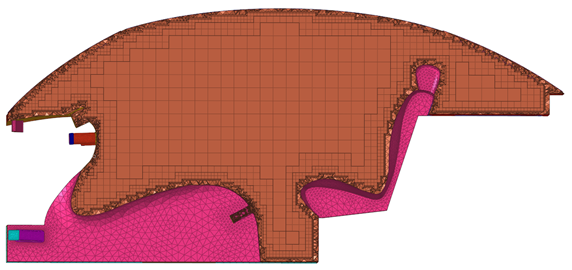
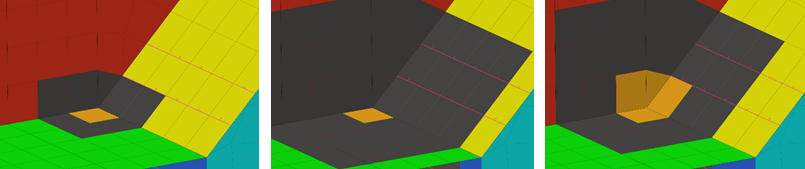
Figure 11. . Resulting mesh when the Core Mesh attribute is set to Hex Dominant. - Fix hexa element quality
- Automatically check and fix the quality of hexa elements based on user criteria using the Solid Mesh Optimization tool. With this tool you can control maximum node movements allowed for quality fix, which reduces the time spent fixing from ~2 hours per part (manual node movement) to few a minutes.
Enhancements
- Layer tetra meshing
- Robustness for layered tetra meshing has been enhanced.
- Boundary layer meshing
- Boundary layer converge in close proximity areas has been improved.
- Miscellaneous
- Elements can be offset directly from a 3D face.
Resolved Issues
- Tetra remeshing issues for shell update.
- Issues with changing the element order during solid meshing.
Model Build and Assembly
New Features
- Manage representations and revisions for part assemblies
- Representation and revision management of part assemblies is now supported. This facilitates usage of Part Browser for use cases such as parts being connected by coincident nodes.
- Concurrent usage of a library shared
- Enhance concurrent usage of a library shared by multiple users with the new library type powered by PostgreSQL.
- Batch mode generation of part representations
- Automated batch mode generation of part representations from a BOM input is supported in the Part Browser. The output is a HyperMesh binary file.
- Library viewer
- Browse the contents of a part library in the new library viewer. Available representations are grouped per revision and can be seamlessly loaded into the session.
Enhancements
- Representation handling
- The midsurface method can be selected prior to generating the common representation. When saving representations, all rows for modifiable columns can be selected via a keyboard shortcut.
- Save As functionality
- Save multiple parts across part assemblies using the "Save As" option accessed in the Part Browser contextual menu.
- Teamcenter visualization BOM support
- The export of Teamcenter Visualization PLMXML’s is now supported with the VizMockup BOM export file type.
- Position parts
- The "Scale" and "Position" options have been added to the Transform tool.
- Configuration management
- When a part assembly is added to a part set or a configuration, a list of child parts is displayed.
- Part Assembly/Part solver deck comments
- Part sets and configurations are written to the solver deck as comments.
Resolved Issues
- Part transformations are incorrect when the transformation matrix is mentioned on CAD/Part.
- Parts saved with shared surfaces results in disassociating shared edges.
Crash and Safety
New Features
- Simulate the positioning of a dummy
- Dummy pre-simulation with the cable method can be performed using the Dummy Pre-Simulation tool. With this tool you can export all of the boundary conditions required to simulate the positioning of the dummy in an input deck. Load simulation results in HyperMesh to update the dummy model.
- Create a mechanism of the selected Finite Element model
- Automatically extract bodies and joints to create a mechanism of the selected Finite Element model using the Mechanism Extraction tool.
- Enable a non-rectilinear translation motion between two bodies
- Enable a non-rectilinear translation motion between two bodies by creating a Cam joint entity in the Mechanism Browser.
Resolved Issues
- Dummy information between *DUMMY_START and *DUMMY_END is empty when reading an input deck.
- Issue with moving a seat forward or backward when a dummy is linked to the mechanism.
- Positioning is occasionally incorrect when using the Pedestrian Impact tool for head impactor contact point positioning.
- When exporting input decks from the Mechanism Browser, the Radioss /BEGIN card is not written correctly.
- Reading HyperMesh files and opening the Dummy Browser occasionally removes the dummy from the display.
Conversion between Solver Formats
Enhancements
- LS-DYNA to Radioss conversion
- *CONSTRAINED_JOINT_STIFFNESS_GENERALIZED converted to /SPRING
- Abaqus to OptiStruct conversion
- *CONNECTOR SECTION conversion to JOINTG.
Model Verification Director
Enhancements
- Launching Model Verification Director
- Launching the Model Verification Director no longer requires an environment variable.
- ProE/Creo
- ProE/Creo and assembly data is now supported.
- CPUs drawn
- For one CPU or Multiple CPUs only 21 HWUs will be drawn.
- Parameter to control location of .hm file
- Control the location of the .hm file after an offset function is executed with a new parameter. By default, the .hm files will be saved under Report folder / Offset_data_folder.
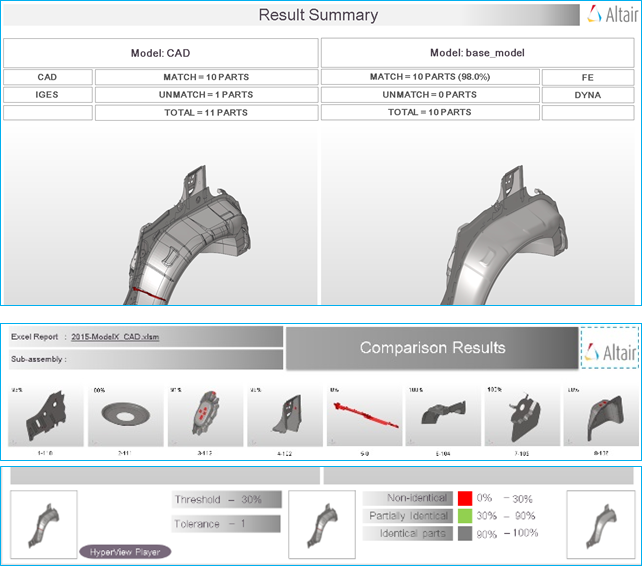
- Performing comparison and verification check
- Using respective browser Comparison and Verifications are executed.
- Comparison checks
- CAD / FE thickness are used as Tolerance for calculating match%.
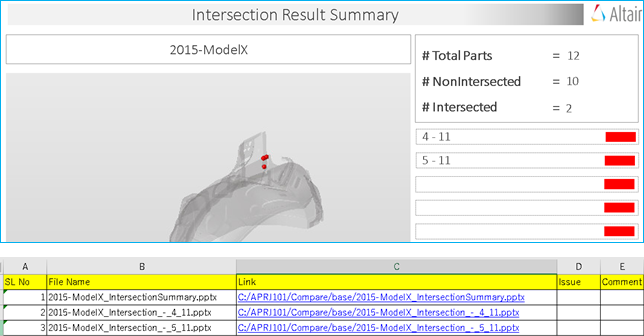
- Intersection checks
- A Part Revision check and Sub-system check has been added to check new revision data and across two sub-systems
- Spotweld check
- The calculation method has been improved to support both CAD and FEM.
- Connection check
- New connection shape mismatch checks for TRIM parts have been added, and use center line CAD as the input. New mismatch checks include: arcweld-mismtach, seam-mismatch, hemming-mismtach, and sealant-mismatch.
- Spot comparison
- PowerPoint and Excel summary reports are now supported.
- Free Part check
- Free Part check must exclude parts less than the minimum area set in the configuration.
Resolved Issues
- Repeated Part set creation results in tcl error if threshold value is set to1.0.
- Batch mode for spot weld check does not work well.
- Transformation matrix breaks for part instances.
- Issue with solid tet support for comparison checks if a single file is selected for the run.
- Some connection checks are huge, and has been fixed by decreasing feature angle.
- Configuration user interface does not close if you do not have access to the Altair Home directory.
- Error received when exporting CSV file.
- Issue with revision check on Catia data.
- CAD and FE folders created by the tool are deleted if the delete-fefiles option is on.
- CAD Part Number is automatically renamed when a blank or special character exist.
- If Mat Vec comp is not found, no thickness needs to be assigned for the CAD.
- Config user interface must not stay on top of window, other window overrides MVD user interface.
API
For a complete list of new, modified and deprecated APIs, refer to the API Programmer’s Guide.
New Features
- New entity types
- New entity types have been added and mapped from old entities, which may require scripting updates. Refer to the API Programmer’s Guide for more details.
- New checks for hm_getelemcheck*
- The checks 'maxlength' and 'minlength' have been added for the hm_getelemcheck* family of commands.
- Detect flanges on both geometry and FE
- Detect flanges on both geometry and FE with the hm_flangedetection command.
- Evaluating mesh patterns and connectivity
- Evaluate mesh patterns and connectivity on an input quad/mixed mesh, and output problem elements onto a mark with the hm_detectmeshpatterns command. This is useful for finding areas of a mesh that do not meet aesthetic requirements.
- Perform model checking
- A new suite of APIs has been added for performing model checking. These may require scripting updates. Refer to the API Programmer’s Guide for more details.
Resolved Issues
- The hm_holedetection family of APIs causes a series of crashes and general issues.
CAD and Solver Interfaces
Abaqus Interface
New Features
- Parts and Instances
- Parts and Instances format input files are supported for import and export only without any modifications to the input file. The hierarchy can be viewed in the Part Browser.
- Contact browser support
- The Contact browser is now available in the Abaqus solver interface, and can be used for auto-contact and detailed specification of contact conditions.
- New Elements
- New elements include: C3D8S, C3D8HS, C3D10S, C3D10HS, ITSUNI, ITSCYL, CCL12, GK3D12M, GK3D12MN, GK3D18, GK3D18N
- New keywords
- New keywords are added for the coverage and some selective examples are: *CLAY PLASTICITY, *BRITTLE FAILURE, *FILM PROPERTY, *FLUID CAVITY behavior, *FABRIC material, *LOW DENSITY FOAM material, *COHESIVE BEHAVIOR for debonding study, *BASE MOTION keywords for vibrational studies
Enhancements
- Support for CCL12 and Gasket elements
- The Gasket element tool supports CCL12 elements, since CC12 elements require mid-side nodes along the stack direction.
- Show stack direction for solid face alignment
- The stack direction is shown with an arrow once the direction has been assigned in the Face Alignment tool.
- *MODEL CHANGE enhancement
- The *MODEL CHANGE keyword supports direct element definition along with element sets.
- Orientation review
- Show the element system and material system for solid elements based on the *DISTRIBUTION TABLE data in the Orientation review tool.
- Updated Keywords
- Keywords that have been updated to include new features with selective examples include: *SELECT EIGENMODES for steady-state dynamics, softening behavior for *CONNECTOR DAMAGE EVOLUTION, default integration point for *SHELL SECTION, element deletion option in *SECTION CONTROLS, additional support for *GEOSTATIC analysis set-up
Resolved Issues
- Cannot contour loads such as pressure, film and so on for elements when using the Contour Loads tool.
- FBD tool in HyperMesh breaks due to ODB reader.
- When exporting *INITIAL CONDITION, datalines are not exported as intended.
- Issue with reading and exporting nested Include files.
- Importing an Abaqus input deck into other solver interfaces causes an application error.
- Issue with element face selection using the Solid Face Alignment tool.
- Cannot organize and map loads in the Loadsteps Browser.
- Formula sets with negative increment creates floating point errors. The starting and ending ID are now swapped from smaller to greater so that the increment stays positive.
- Model Checker for Abaqus cannot be accessed from the Search tool.
- The Face Selection panel disappears when creating *SURFACE.
- Gasket elements surface are not recognized with face ID as SPOS/SNEG.
- The original name for *DISTRIBUTION and *DISTRIBUTION TABLE are not retrained upon import.
- The dataline for *RIGID BODY keyword has unnecessary comma.
- Importing Abaqus explicit input decks causes segmentation error.
- Clash with element flagging between C3D8S and CCl12 elements.
- ELSET that are referenced in a *FASTENER is lost.
- Acoustic elements AC3D15 and AC3D20 are lost in the standard 3D profile.
AcuSolve Interface
All new features, enhancements, and resolved issues in the AcuSolve solver interface from 2017.2.4 and 2017.3 hotfix versions are available in version 2019.
New Features
- DENSITY_MODEL
- New material density types include: Isentropic, Piecewise Linear, Cubic Spline, and User Function.
- SPECIFIC_HEAT_MODEL
- New material specific heat types include: Piecewise Linear, Cubic Spline, and User Function.
- VISCOSITY_MODEL
- Nw material viscosity types include: Ramped, Power Law, Bingham, Carreau, Piecewise Linear, Cubic Spline, and User Function.
- CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL
- New material conductivity types include: Constant Prandtl Number, Ramped, Piecewise Linear, Cubinc Spline, User Function, Constant Anisotropic, Piecewise Linear Anisotropic, Cubic Spline Anisotropic, and User Function Anisotropic.
- GRAVITY, VOLUME_HEAT_SOURCE, MASS_HEAT_SOURCE
- body_force commands support multiplier_function and user_function.
- AUTO_WALL
- The option auto_wall = ON/OFF is added to Wall boundary condition. This option is hidden under Advanced Features, and is turned ON by default. When auto_wall = on, mesh motion and reference frame related settings need not be specified on the Wall boundary, and will not be accessible under SIMPLE_BOUNDARY_CONDITION. The auto_wall feature can also be used to model interface surfaces and internal surfaces. When auto_wall = ON, SURFACE_OUTPUT commands are automatically generated by the solver. Additional SURFACE_OUTPUT command is generated by modifying the default output frequency settings.
- THERMAL_SHELL
- Model heat transfer through 2D thermal shells.
- FAN_COMPONENT
- Model flow through a radial or axial fan component via body forces without the need for modeling a realistic fan geometry.
- HEAT_EXCHANGER_COMPONENT
- Model flow and heat transfer through a heat exchanger component.
- ELEMENT_BOUNDARY_CONDITION
- Specification of heat_flux, convective_heat_flux, and radiation_heat_flux on Walls.
- SURFACE_INTEGRATED_CONDITION
- Specification of integrated boundary conditions for temperature and mass_flux at Inflow and Outflow boundaries.
- ELEMENT_OUTPUT
- Output of quantities averaged over a volume of elements. This option is available under each Volume component.
- Discrete Ordinate Radiation Model
- Model heat transfer effects due to participating media radiation using Discrete Ordinate Model. This option is available under PROBLEM_DESCRIPTION card.
- Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian (ALE)
- New mesh motion type under PROBLEM_DESCRIPTION card, which allows arbitrary mesh motion. Useful for FSI applications.
- Temperature Boundary Condition Type = None
- Temperature BC at a Wall can be set to None under Simple_Boundary_Condition. This is useful when advanced thermal BCs need to be specified via Element_Boundary_Condition.
- Reference Temperature Multiplier Function
- Specification of Multiplier Function for Convective Heat Flux Reference Temperature on a Wall.
- Velocity Standard Deviation
- Standard deviation of x/y/z velocity components are added to the types of surface output quantities under RESPONSE_VARIABLE.
- Advanced Solver Settings
- Access advanced settings for individual equation’s STAGGER command (min/max number of stagger iterations, linear solver iterations, projection and pressure projection flags).
- Inflow Velocity Type
- Specify inflow velocity in cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems.
- Wall Velocity Type
- Specify velocity of a moving wall in multiple ways - Cartesian, Spherical, Cylindrical, Normal, and Zero.
- Active Type
- active_type is added to SIMPLE_BOUNDARY_CONDITION. Used in applications with mesh motion.
- Curve Fit Variables in NODAL_BOUNDARY_CONDITION
- Additional variables are added under curve_fit_variable in NODAL_BOUNDARY_CONDITION (x/y/z coordinate, reference coordinate).
- GUIDE_SURFACE
- Ability to specify a set of 2D elements as a guide for mesh motion.
- FREE_SURFACE
- Model a free surface by applying appropriate mesh motion boundary conditions on the surface nodes.
Enhancements
- Mixed Topology Export (VOLUME_SET and SURFACE_SET)
- Option to export AcuSolve input file in a new format. Mixed topology components containing multiple element topology types (quad4/tria3, tetra4/hex8/pyramid5/penta6) are exported as independent surface_sets and volume_sets, which are then referenced under solver commands such as ELEMENT_SET, SIMPLE_BOUNDARY_CONDITION, and so on.
- NODAL_INITIAL_CONDITION
- Set unique initial values per component or node set for each variable, such as initial liquid volume fraction, or initial temperature. This is useful in multiphase and heat transfer applications.
- NODAL_BOUNDARY_CONDITION
- Specify nodal boundary condition at individual nodes or node sets. This is useful for setting reference pressure node in natural convection applications.
- Default Multiphase Materials
- Default material models are readily available for use with Multiphase Levelset approach (AirWater_Leveset_HM) and Multiphase Algebraic Eulerian approach (AirWater_Eulerian_HM). These material models can be used as a starting point to create other multiphase material combinations.
- AcuFieldView Launcher
- AcuFieldView launcher has been added in two locations 1) Adjacent to AcuSolve Job Launcher in the toolbar, 2) tab after launching the simulation via AcuSolve Job Launcher.
- Component colors
- New components of the same type are assigned unique colors when created from the utility.
Known Issues
The following known issues will be addressed in a future release as we continuously improve performance of the software:
- New features added to the AcuSolve user profile are not currently supported by the .inp reader. You should not import input decks written from AcuConsole or from HyperMesh 2019.
Resolved Issues
- Data type of Redistribution Factor under SOLAR_RADIATION_PARAMETERS card has been changed from Integer to Real. This will require deleting and recreating this global card when loading HM models created with 2017.2.4 and 2017.3 into v. 2019 or newer.
- Mesh_Displacement_Type will be exported as “none” for all SIMPLE_BOUNDARY_CONDITION cards when performing shape optimization simulations (users need not do this manually).
- Import bugs in the NODAL_INITIAL_CONDITION card.
- Supervised Training data in DESIGN_VARIABLE does not accept duplicate values.
CAD Interface
New Features
- New CAD readers
- Inventor 2018
- New CAD writers
- Inspire 2018.1
- Part and part assembly creation during CAD import
- Parts and part assemblies are automatically created during CAD import to allow for a more seamless and streamlined model build workflow, with fewer steps and improved robustness.
- Specify unit system during CAD import and export
- Select a target unit system during CAD import and export to allow any CAD file to be imported without requiring the user to know the unit system defined in the incoming file.
Enhancements
- Renamed Tribon reader
- The Tribon reader has been renamed to AVEVA Marine.
- Edit additional PDM attributes
- The following PDM attributes can now be modified: PDM_MeshFlag, PDM_MID, PDM_PID and PDM_Revision.
- Read only assembly-level geometry
- Read only assembly-level geometry contained within assembly files, which helps when loading representations within the Part browser.
- Read coordinate systems from NX files
- Coordinate systems are optionally read from NX files via the native reader.
- Read infinite planes from CATIA files
- Infinite planes are optionally read from CATIA files.
- Support for JT ultra-lightweight precise (ULP) tessellations
Resolved Issues
- Performance issues when importing STEP files containing many polylines.
- Could not properly read JT assembly files with relative paths to children parts.
- Issues with general robustness and performance.
Exodus Interface
Resolved Issues
- Issue with importing RBE2, RBE3 and ECHO cards.
- Import mixed element type in one component is resolved by splitting to elements into different blocks.
- Issue with importing legacy models.
- Performance issue during import and GUI creation of “Side Set”.
- Solver Browser cleanup removed non-applicable items from the browser.
FEKO Interface
New Features
- New Feko solver interface
- The Feko solver interface improves the transfer of mesh element and material data between HyperMesh and Feko.
- Import and export of Feko mesh and media data
- The import and export of Feko mesh and material data is supported through the import and export of the *.fhm file format. This new file format contains the mesh element data, the material definitions, and the assignment of material properties to the mesh elements.
- Supported mesh elements
-
HyperMesh Feko Bar2 Straight wire segments Bar3 Curvilinear wire segments Tria3 Flat triangles Tria6 Curvilinear triangles Tetra4 Tetrahedra - Supported Feko media definitions
- Feko supports the definition and assignment of several Feko medias.
LS-DYNA Interface
New Features
- New LS-DYNA R9.0 solver interface
- The LS-DYNA R9.0 solver interface is introduced along with related major keyword updates.
- New entity type for *ALE keywords
- *ALE keywords are now treated as independent entities, whereas in the past they were mapped to the Group entity type.
- New entity type for *INTERFACE keywords
- *INTERFACE keywords are now treated as independent entities, whereas in the past they were mapped to the Group entity type.
- New entity type for *TERMINATION keywords
- *TERMINATION is a new keywords, and is treated as independent entities.
- New Keywords
- An estimated 70 new keywords have been added, and are part of the following LS-DYNA keyword groups: *CONTACT; *DATABASE; *ELEMENT; *INTERFACE; *LOAD; *MAT; *PARAMETER; *SENSOR; *TERMINATION.
- Support of *PARAMETER_LOCAL and *PARAMETER_EXPRESSION_LOCAL
- LOCAL parameters are now available.
- ID Parametrization
- *PARAMETER has been extended to the parameterization of ID for the LS-DYNA keywords created using Component, Material, Property and Curve entities. The parametrization of the IDs for those entities is also possible in any keywords where such entities are referenced.
- Mass Summary browser
- View model mass, center of gravity, and inertia details in the Mass Summary browser.
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- An estimated 90 keywords have been updated, and are part of the following LS-DYNA keywords groups: *ALE; *CONSTRAINED_INTERPOLATION; *CONTACT; *CONTROL; *DATABASE; *ELEMENT; *EOS; *INITIAL_VELOCITY; *INTERFACE; *LOAD; *MAT; *SECTION; *SENSOR
- Penetration Check tool enhancements
- The square edges contact option, activated by the SHLEDG or SRNDE attributes is now considered in the Penetration Check Tool when this option is enabled in the *CONTACT or *CONTROL_CONTACT keywords.
- Model Checker enhancements
- The Model Checker infrastructure and functionalities have been improved for a better user experience.
- Removed Keyword 960 user profile
- The Keyword960 user profile has been completely removed from the installation.
- Find entities attached to components
- The Recursive option has been added in the Find Connectivity tool to help isolate and find entities attached to selected components. This new functionality will also help you to automatically find parts until all connected parts are found.
- Removed tool
- The following tools, previously accessible in the Tools menu and Utility browser, are now completely removed from HyperMesh: Set Browser, Create Part, Clone Part, Material Table, Component Table.
- Manage the printing of HyperBeam messages
- An import option has been added to enable or disable the printing of HyperBeam messages. By default, this option activated and HyperBeam messages are not printed.
- Export options enhancements
- The Export option is now set to Custom by default in the Export browser.
Resolved Issues
- Issue with Model Checker checks related to property and material assignment to the component, when *PART_COMPOSITE is used.
- Reader issue when reading a deck containing *CONTACT_AUTOMATIC_BEAM_TO_SURFACE.
- Issue with reader behavior for the *DEFORMABLE_TO_RIGID keyword. It is also updated to the R9.0 manual.
- Parameter names were exported left justified, but are now exported and right justified in the parameter name column. This change handles use cases in which parameter names contain a blank, and the parameter is inside an encrypted keyword.
- Issue with head of edge vector values when creating an infinite plane cross-section.
- Selection of constrained nodal rigid body IDs was not allowed in the *INITIAL_VELOCITY_RIGID_BODY keyword.
- Material direction vectors for composite parts were not being displayed correctly.
MARC Interface
Enhancements
- Damping card support
- The DAMPING solver damping card is now supported. This card can be imported and exported, and can be accessed from materials.
- Complex values in fixed displacements
- Complex values in fixed displacement cards can be imported and exported. Marc model files with displacements defined in real and imaginary phase can now be imported and exported successfully.
- Entity Editor support
- The Entity Editor as now supported, and all Marc solver entities can be accessed from the Entity Editor.
Nastran Interface
New Features
- Generate 1D PLOTELs from DMIG grids
- The PLOTEL from DMIG tool enables you to generate 1D PLOTELs from DMIG grids. You can then use an exported solver deck with PLOTELs to visualize DMIG in HyperView.
- NX Nastran with comments written from FEMAP
- The following formats are supported for FEMAP comments written to NX Nastran models: $ Femap with NX Nastran Property: name and $ Femap Property: name.
- New keywords
- New bulk cards include: NOLIN1, NOLIN2, NOLIN3, NOLIN4 and NLRGAP. These can be referred in NONLINEAR subcase selection for transient response analysis P2G, B2PP, M2PP and A2GG DMIG selection support.
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- WR3R, WR4R and WRHR options in RSPINR card.
- Create PARAM, CASE CONTROL and GLOBAL OUTPUT
- Create PARAM, CASE CONTROL and GLOBAL OUTPUT in the Model Browser using the Create option in the right-click context menu.
- Manage DMIG
- Review DMIG and visualize in spider form.
- Expand formula sets on import
- The Expand formula sets on import option has been added to the Import Browser.
- BCPARA
- The BCPARA card can be defined in the browser similar to BCONPRG.
- BCONECT
- The same BCONECT card can be referenced by different BCTABL1 cards.
- BCONECT
- The BCONECT card now allow the same BCBODY1 to be selected for the slave and master.
- Create sets based on PATRAN groups in decks
- The Create sets based on PATRAN groups in deck solver option has been added to the Import browser.
- Export format export as a new solver
- The Free format export as new solver option has been added to the Export Browser.
- New warning check
- The warning, Loadcol has two or more different load types, has been added to the Model Checker.
- Performance improvements
- Performance improvements of up to 70% when using the By HM comments import option to import an input deck that contains the direct property "HMDPRP".
Resolved Issues
- All critical defects resolved in 2017 hotfixes are included in this release.
- Import issue of ACCEL I/O card with following form (SORT2,PHASE) = 1.
- PBEAM cards that has extension lines with different HyperBeam comments is not read correctly.
- Incorrect node ID is printed for for missing CP/CD.
- 1D element length does not consider offset value.
- PSHELL and PSHEAR with the same ID do not stay the same on import.
- Other critical defects have been resolved.
OptiStruct Interface
New Features
- Generate 1D PLOTELs from DMIG grids
- The PLOTEL from DMIG tool enables you to generate 1D PLOTELs from DMIG grids. You can then use an exported solver deck with PLOTELs to visualize DMIG in HyperView.
- New entity type for Rigid Walls
- RWALL keywords were originally mapped to the Group entity type, but HyperMesh now treats those keywords as an independent entity, with its own ID, icon, and graphics.
- New keywords
- TABLEMD bulk card defines multidimensional tabular functions.
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- NLADAPT, STABILIZ activates static stabilization in a nonlinear static analysis.
- Updated keywords - PARAM card
- NLSNSINC triggers incremental sensitivity analysis for nonlinear static subcases.
- Updated keywords - SYSETTNG card
- RESVEC option controls the generation of extra global residual vectors for Component Mode Synthesis (CMSMETH).
- Updated keywords - I/O cards
- HDF5 format output request.
- Create PARAM, CASE CONTROL and GLOBAL OUTPUT
- Create PARAM, CASE CONTROL and GLOBAL OUTPUT from Model Browser using the Create option in the right-click context menu.
- Review DMIG
- Review DMIG and visualize in spider form.
- Ply orientation support for PCOMPLS property NLGEOM and IMPDYN analysis types
- The NLGEOM and IMPDYN analysis types are removed from the OptiStruct solver interface. These analysis types can be activated using the environment variable HM_ACTIVATE_NLGEOM_IMPDYN = YES.
- Performance improvements
- Performance improvements of up to 70% when using the By HM comments import option to import an input deck that contains the direct property "HMDPRP".
Resolved Issues
- All critical defects resolved in 2017 hotfixes are included in this release.
- OptiStruct reader crashes due to embedded blanks in PARAM cards.
- When there are more than 7 panels to define RADSND, continuation cards are created by HyperMesh, which causes an OptiStruct syntax error due to incorrect format.
- STRESS TOP TOPN field is not exported properly.
- Entity Editor does not show available SET_GRID when defining SET_ID on DISP or PRESSURE output request cards.
- Many other critical defects are resolved in this release.
PAM-CRASH 2G Interface
New Features
- New PAM-CRASH 2017 solver version
- Pamcrash2G2017 solver profile is introduced, and offers new keywords and major keyword updates related to this new solver version.
- New entity for SECFO keywords as Cross Sections
- SECFO keywords were originally mapped to the Group entity type, but HyperMesh now treats these keywords as independent Cross Section entities with a unique ID, icon and graphics.
- Model Checker
- The Model Checker tool has been added to the PAM-CRASH 2G solver interface, and offers specific checks for solver validity categorized as ERROR, WARNING and INFO.
- New Keywords
- An estimated 35 new keywords are added in HyperMesh 2019. These new keywords are part of the following keywords categorises: PART, MATER, CNTAC, CONTROL, Constraint, SENSOR, SECFO, ELEMENT, PYFUNC, BAGIN-CHAMBER sub-keywords.
- Support of mapping files keywords
- The IMPFIL, IMPORT and EXPORT mapping file keywords with sub-keyword TRANSFORMATION can be created using the Position and Transformation entities.
- Support of picking definition keywords
- The picking keywords PICEXP and PICIMP from 2015 onward and PICK in 2012 to 2014 user profiles can be created using the Position entity.
- New Mass Summary browser
- The Mass Summary browser was added to enable you to review model mass, center of gravity, and inertia details.
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- An estimated 130 keywords are updated in this new HyperMesh version. These keywords are part of the following keywords categories: PART, MATER, CNTAC, CONTROL, CONSTRAINT, SENSOR, SECFO, SAFETY, ELEMENT, PYVAR, FUNCT, PLOT-OUTPUT, BAGIN-CHAMBER sub-keywords.
- Accurate Mass Calculation
- The mass calculation logic has been improved to match the solver behavior, NSMAS and NSMAS2 accounted as nonstructural mass.
- Pamcrash2G2010-2011 solver interface
- The Pamcrash2G2010-2011 solver interface is removed, but is still available in the installation; however, it will no longer be maintained.
- Removed tools
- The following tools, previously accessible in the Tools menu and Utility browser, are removed from HyperMesh: Set Browser, Create Part, Clone Part, Material Table, Component Table.
- Improved reading and evaluation of Python keywords
- The reading and evaluation of the PYFUNC and PYVAR Python keyword's expressions and IDs have been improved. Complex expressions are not editable in the HyperMesh session, and the expression is not evaluated when its child variables are missing.
- FUNCT enhancements
- Function (FUNCT) supports reference of the python function keyword PYFUNC when FUNTYP is EPYFUN.
- Format of data output
- Data output for all the keywords is right justified except for sub-keyword strings.
- Improved import messages
- Improved import messages with the keywords CNTAC, MATER, Include files, HyperBeam, Airbag sub keywords and so on.
- Removed obsolete keywords
- Obsolete keywords such as RWALL_KIN_CHECK, ADAPT, SUBTA, SOLID4N, SPH and data are unsupported upon import if present in input deck.
- Removed obsolete SPH control card
- Obsolete SPH control card are removed, and the equivalent SPCTRL is available.
Resolved Issues
- Keyword BELTS are mapped to elements instead of beam section collector when using the Entity Editor to select IDNODs.
- Unable to import models that contain Shell and Beam elements that have the same element ID.
- OTMCO supports multiple weight factor on GES when using the Entity Editor to update WEIGHT & DOFCOD.
- Issues related to the creation of INCLU keyword from the Solver Browser.
- Issues with importing/exporting old solver decks that have MATER & SPRGBM keywords handled.
- Issue exporting when GES data has mixed range and is listed under GROUP keyword.
- Issue with FE-Overwrite when working with GES data across keywords (example: BAGIN & PREFA).
- Issue with enabled option in Export browser to write HyperMesh comments into output files.
Permas Interface
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- $INERTIA -CORIOLIS & ROTATION
Resolved Issues
- $SYSTEM and $COMPONENT card is imported by default.
- $GEODAT SHELL properties are retained on export.
- Node coordinates exported with double precision.
- Model checker added to find entities with >40 characters.
- $ELSYS RSYS supported for sets.
- $SUPRESS DOFTYPE=DISP export issue.
RADIOSS Interface
New Features
- New Keywords
- An estimated 50 new keywords are added in this HyperMesh version and enhance the Radioss keywords support.
- New entity type for Accelerometers
- The /ACCEL keyword was originally mapped to the Sensor entity type, but is now mapped to an independent entity, with its own IDs, icon and graphics.
- New entity type for Mass
- The /ADMAS keyword was originally supported as elements, but is now mapped to an independent entity, with its own IDs, icon and graphics. A specific graphic review for /ADMAS/TYPE5 is also available to review the nodal mass distribution. Along with this development, all /ADMAS types are now supported in HyperMesh.
- New entity type for Elements Clusters
- /CLUSTER keywords are now supported in HyperMesh, and are mapped to an independent entity, with its own IDs, icon and graphics.
- New entity type for Failure Models
- /FAIL keywords were originally mapped to the Property entity type, but are now mapped to an independent entity, with its own IDs and icon.
- New entity type for Optimization keywords
- Optimization keywords are now supported in HyperMesh inside the Optimization browser, and are treated as special entities. The optimization keywords are imported and exported in the Radioss .radopt file.
- New entity type for Rigid Walls
- /RWALL keywords were originally mapped to the Group entity type, but are now mapped to an independent entity, with its own IDs, icon and graphics.
- New entity type for Positions and Transformations
- /TRANSFORM keywords were originally mapped to the System Collector entity type, but are now mapped to an independent Transformation entity. Additionally, the Position entity is introduced as a collector of the Transformation entities that are applied to the same content.
- Support of Submodels
- //SUBMODEL keyword is now supported in HyperMesh. ID offsets rules and transformation rules on submodels are also implemented. All sets of type SUBMODEL are also supported.
- Support of XELEM elements
- /XELEM elements are newly implemented in this HyperMesh version.
- Creating transformations and positions
- Create Transformation and Position entities more seamlessly using the Create and Edit Position/Transformation tool, which replaces the previously existing Transformation Manager.
- New Mass Summary browser
- The Mass Summary browser was added to enable you to review model mass, center of gravity, and inertia details.
Enhancements
- Updated keywords
- An estimated 40 keywords are updated regarding the latest 2017 and 2018 Radioss solver versions.
- /BEGIN card enhancement
- The definition of the unit systems in the /BEGIN card support has been improved for a better user experience. The support of /BEGIN cards in Include files is also improved.
- /TH card enhancement
- The definition of the output variables into /TH keywords is now given as a list selection.
- Material features added into compatible materials
- Material features keywords (/EOS, /LEAK/MAT, /THERM_STRESS, /VISC/PRONY) were originally mapped to the Property entity type, but the definition of these keywords is now directly implemented into their compatible material keywords using the Entity Editor.
- Composites modeling enhancements
- Composites modeling now supports the usage of the new Radioss composites keywords introduced into the Radioss 2017 version.
- Review SETs graphically
- Improvements have been made for the review of SETs based on the type of set. For example, a /GRNOD/PART will highlight the nodes of the referred components instead of highlighting the components.
- Accurate mass calculation
- The mass calculation logic has been improved to match the solver behavior.
- Penetration check enhancements
- The Penetration Check tool now enables you to check Radioss Interface TYPE24. Additional improvements have also been made in the penetration’s calculation for second order elements.
- Model Checker enhancements
- The Model Checker infrastructure and functionalities have been improved for a better user experience.
- Importing sets of subtype /SUBSET and /PART
- Sets of subtype /SUBSET and /PART are not imported as a formula set when all referenced subset or part IDs are positive.
- Removed tools
- The following tools, previously accessible in the Tools menu and Utility browser, are removed from HyperMesh: Set Browser, Create Part, Clone Part, Material Table, Component Table.
- Manage the printing of HyperBeam messages
- An import option has been added to enable or disable the printing of HyperBeam messages. By default, this option activated and HyperBeam messages are not printed.
- Find entities attached to components
- The Recursive option has been added in the Find Connectivity tool to help you isolate and find entities attached to selected components. This new functionality will also help you to automatically find parts until all connected parts are found.
Resolved Issues
- Could not create or import multiple /FVMBAG/MODIF cards defined in the engine file.
- Could not read /MAT/LAW60 with a number of functions less than 5.
- Sets of type GENE are created incorrectly in the Entity Editor.