I-deas
I-deas specific checks used to calculate element quality for 2D and 3D elements.
Additional element checks not listed here are not part of the solver’s normal set of checks, and therefore use HyperWorks X check methods.
2D and 3D Element Checks
- Stretch (Aspect Ratio)
- Stretch is evaluated differently depending on whether the element is
triangular or quadrilateral:
- For trias, the radius of the largest circle that fits within the
element is divided by the longest edge, then multiplied by the
square root of 12.
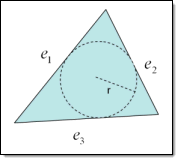
Figure 1. Stretch for Trias - For quads, the minimum edge length is divided by the maximum diagonal length. The result is multiplied by the square root of 2.
Note: The inverse of stretch displays on-screen in HyperWorks X as the aspect. - For trias, the radius of the largest circle that fits within the
element is divided by the longest edge, then multiplied by the
square root of 12.
- Chordal Deviation
- Largest distance between the centers of element edges and the associated
surface. Second order elements return the same chordal deviation as
first order, when the corner nodes are used due to the expensive nature
of the calculations.
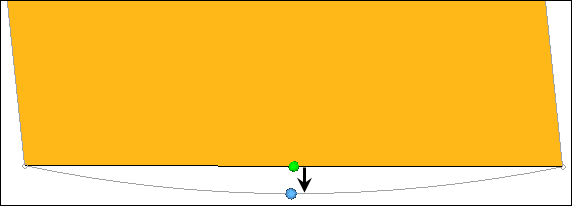
Figure 2. Chordal Deviation - Jacobian
- Deviation of an element from its ideal or "perfect" shape, such as a triangle’s deviation from equilateral. The Jacobian value ranges from 0.0 to 1.0, where 1.0 represents a perfectly shaped element. The determinant of the Jacobian relates the local stretching of the parametric space which is required to fit it onto the global coordinate space.
- Length (min)
- Minimum element lengths are calculated using one of two methods:
- The shortest edge of the element. This method is used for non-tetrahedral 3D elements.
- The shortest distance from a corner node to its opposing edge (or face, in the case of tetra elements); referred to as "minimal normalized height".
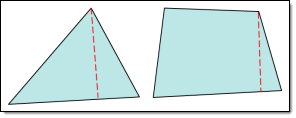
Figure 3. Length (min) - Skew
- Deviation of an element’s corners from 90 degrees (for quads) or 60 degrees (for trias).
- Taper
- Taper ratio for the quadrilateral element is defined by first finding
the area of the triangle formed at each corner grid point.
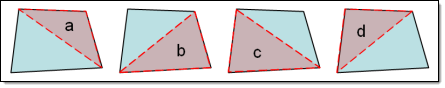
Figure 4. Taper - Warpage
- The amount by which an element, or in the case of solid elements, an element face, deviates from being planar. Since three points define a plane, this check only applies to quads. The quad is divided into two trias along its diagonal, and the angle between the trias’ normals is measured.
3D Element Only Checks
- Stretch (volume aspect ratio)
- Stretch is evaluated differently depending on whether the element is a
tetrahedron, Wedge, Brick, or Pyramid.
- Tetras
- The radius of the largest sphere that fits within the element is divided by the longest edge. This value is then multiplied by the square root of 24.
- Wedges
- Each face is evaluated for its 2D stretch, and the worst value is reported. This means that the value reported for vol AR should always be the same as that reported for aspect.
- Bricks
- The minimum edge length is divided by the maximum diagonal length. The result is multiplied by the square root of 3.
- Pyramids
- No check is defined, so HyperWorks X performs its standard check in which each face is evaluated as a 2D object and the worst result reported.