Symmetry Panel
Use the Symmetry panel to create symmetries that influence handles, morph volumes, domains, blocks, rwalls, and shapes.
Location: Tool page > HyperMorph module
Changes made on one subpanel do not affect the other, and are persistent so that you can switch freely between subpanels without losing any settings already made.
HyperMesh supports reflective and non-reflective symmetries.
Symmetries can be combined, but you must be careful not to create confusing symmetrical arrangements. Symmetries can also be applied to unconnected domains. In this case, the symmetric handle linking works the same as that for connected domains, but the influences between handles and nodes for non-reflective symmetries do not extend across to all domains.
Create Subpanel
| Option | Action |
|---|---|
| name = | Enter a name for the new symmetry that you wish to create. Alternatively, click the button twice to select an existing domains that you wish to update. Change the other settings as desired, and then click update to save the changes. |
| domains | Select the domain(s) that the new symmetry is part of. |
| morph volumes & mapping | By default, symmetries do not affect morph volumes or map to geom operations. If you wish the symmetry to affect morph volumes and mapping operations as well as domains, select this checkbox. Symmetries that affect morph volumes will affect all of the morph volumes in the model. Symmetries that affect mapping operations will affect all mapping operations, even if there are no domains in the model. |
| approximate / enforced | For reflective
symmetries (1-, 2-, or 3-plane, or cyclical), choose how strict
the symmetric requirements should be.
Note: Handles created due to the enforced
option may not be located on any mesh, however, they will
always be assigned to the nearest domain and will affect
nodes in that domain.
|
| (symmetry type switch) | Use this switch to pick the type of symmetry you wish to create. |
| multilateral / unilateral | For reflective
symmetries (1-, 2-, or 3-plane, or cyclical), choose how
different sides of the symmetry interact with each other.
|
| syst | Select a coordinate system with which the symmetry is aligned. |
| align with: | Define which axis of the chosen system the symmetry is aligned with: thedefault axis, or one of its x/y/z axes. |
| size = | Specify a size for the symmetry's visual icon. This only affects the appearance of the symmetry icon in the modeling window. |
| color | Select a color for the symmetry's icon. |
Update by Domain Subpanel
| Option | Action |
|---|---|
| domain | Select the desired domain. Only one domain can be selected at a time. |
| symmetries | Select the symmetries that you wish to assign to the currently selected domain. You may pick multiple symmetries. |
Command Buttons
| Button | Action |
|---|---|
| create | Create a new symmetry based on the settings you have specified in the create subpanel. |
| update | Update the selected symmetry to use the settings currently specified in the create subpanel. |
| review | On the create
subpanel, this displays the symmetry links between the handles
for the selected symmetry. On the update by domain subpanel, review loads the symmetries associated with the selected domain into the symmetry collector. |
| refresh | Update the symmetry
links between handles. Note: This may cause
different handles to be linked and new handles to be created
if the model was morphed while the symmetries were inactive
or if symlinks was turned off.
|
| reject | Reject the creation of an entity (such as a shape or constraint). This differs from undo because undo only undoes the movement of nodes; rejecting an entity can also undo node movements, but its primary function is to delete an entity that was just created. |
| return | Exit the panel. |
Symmetry Types
HyperMesh supports reflective and non-reflective symmetries.
Reflective Symmetries
Reflective symmetries link handles in a symmetric fashion so that the movements of one handle will be reflected and applied to the symmetric handles. You can also use reflective symmetries to reflect morphs performed on domains when using the alter dimensions: radius, curvature, and arc angle tools or any map to geom operation. To turn the reflection of morphing operations off, clear the symlinks check box or inactivate the symmetry in the Morph Options panel.
- Unilateral Symmetries
- Have only one side that governs the others, but not vice versa. For example, handles created and morphs applied to handles on the positive side of the symmetry are reflected onto the other side or sides of the symmetry, but handles created or morphs applied to handles on the other side or sides of the symmetry are not reflected.
- multilateral symmetries
- All sides govern all other sides. For example, a handle created or a morph applied to a handle on any side is reflected to all the other sides.
- Approximate symmetries
- May contain handles that are not symmetric to other handles. For example, handles created on any side of the symmetry are not reflected to the other sides. This option is best for asymmetrical, but similar, domains or for a cyclical symmetry applied to a mesh that sweeps through an arc but not a full circle.
- Enforced symmetries
- Cannot contain handles that are not symmetric on all other sides. For example, handles created or deleted on any side of the symmetry are created or deleted on the other sides so that the symmetry is maintained. When a reflective symmetry is created with the enforced option, additional handles may also be created to meet the enforcement requirements.
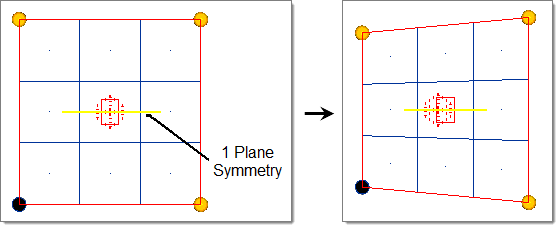
- One Plane
- A mirror is placed at the origin perpendicular to the selected axis (default = x-axis).
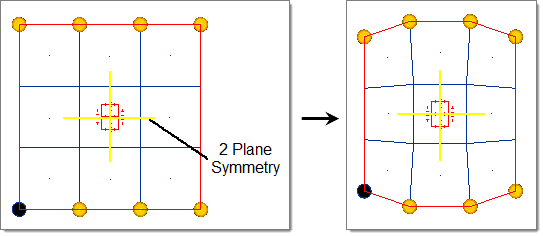
- Two Plane
- Two mirrors are placed at the origin perpendicular to the selected axis and the subsequent axis (that is x and y, y and z, z and x) (default = x and y-axis).
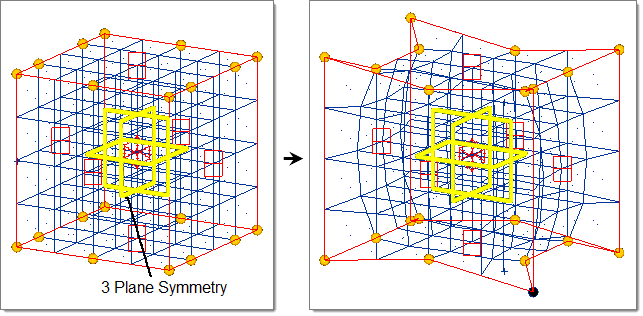
- Three Plane
- Three mirrors are placed at the origin perpendicular to all three axes.
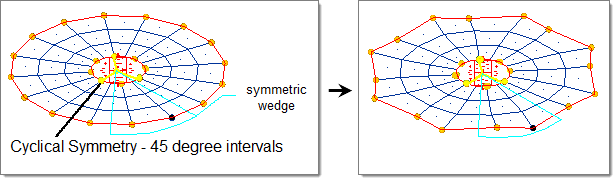
- Cyclical
- Two mirrors are placed along the selected axis (default = z-axis) and run through the origin with a given angle in between that is a factor of 360. The result is a wedge that is reflected a certain number of times about the selected axis.
Non-Reflective Symmetries
Non-reflective symmetries are linear, circular, planar, radial 2D, cylindrical, radial + linear, radial 3D, and spherical. These change the way that handles influence nodes as well as link the symmetric handles so that the movement of one affects the others. You can control whether or not a handle perturbation is applied to symmetric handles for both reflective and non-reflective symmetries by selecting or clearing symlinks or making the symmetries active or inactive in the Morph Options panel. However, the unique handle to node influences for non-reflective symmetries can only be turned off by making the symmetry inactive.
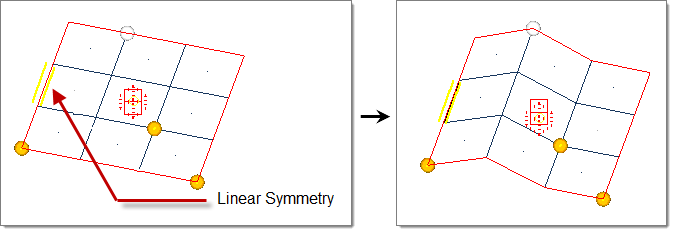
- Linear
- Handle acts as a line drawn through the handle location parallel to the selected axis (default = x-axis).
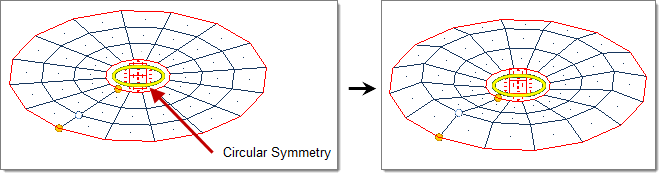
- Circular
- Handle acts as a circle drawn through the handle position about the selected axis (default = z-axis).
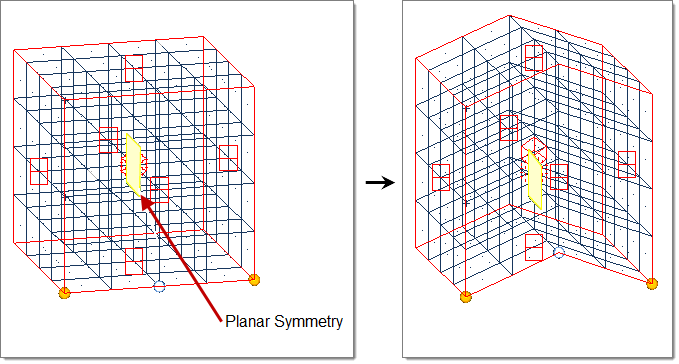
- Planar
- Handle acts as a plane drawn through the handle location perpendicular to the selected axis (default = x-axis).
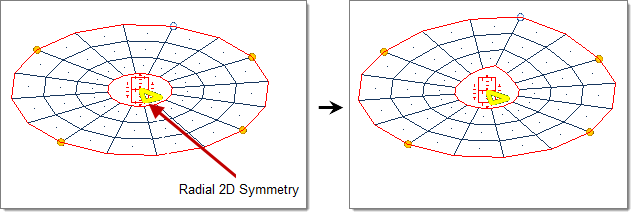
- Radial 2D
- Handle acts as a ray drawn through the handle position originating from and extending perpendicular to the selected axis (default = z-axis).
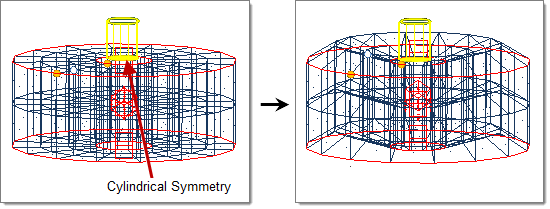
- Cylindrical
- Handle acts as a cylinder drawn through the handle position about the selected axis (default = z-axis).
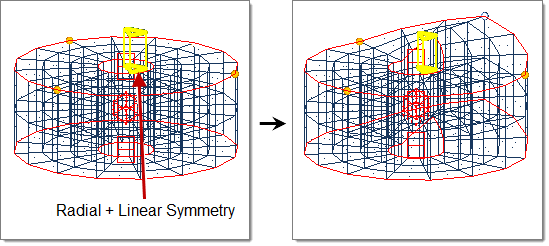
- Radial + Linear
- Handle acts as a plane drawn through the handle position extending from the selected axis (default = z-axis).
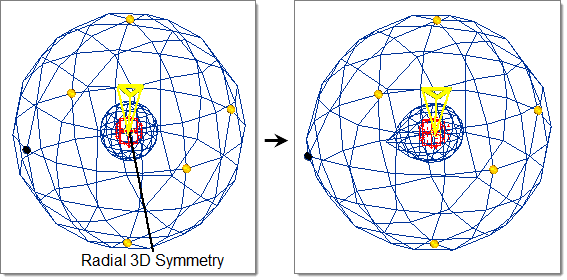
- Radial 3D
- Handle acts as a ray drawn through the handle position originating from origin.
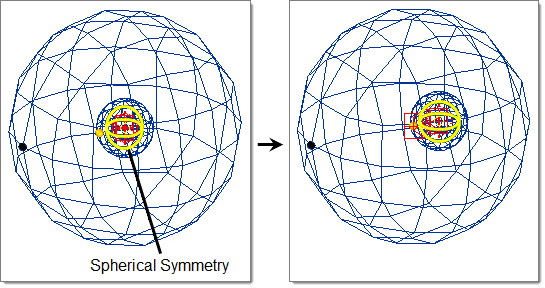
- Spherical
- Handle acts as a sphere drawn through the handle position centered on the origin.