Rigid Body Mesh
Use the Rigid Body Mesh tool to create a quick mesh to represent the topology of a rigid object.
Rigid bodies are surfaces that are expected to be treated as undeformable in the solution. One example of a rigid body is in metal-forming. When modeling the results of a die pressing down on a metal sheet, it’s important to model the shape of the die because that determines the shape of the metal sheet after being pressed. However, during a forming analysis the stresses and deformations of the die itself are not of interest, only those of the formed metal sheet. Other applications for rigid bodies include the impactors used in vehicle crash simulation.
A mesh that accurately represents the rigid geometry is important for such simulations to allow the solver collision detection routines to work effectively and accurately. Since stress and deformation of the rigid body are not calculated by the solver, the rigid body mesh focuses on accurately modeling the shape of the body rather than on producing a high-quality mesh. To this end, it uses the same faceting and shading routines that are used for drawing the model graphics. The resulting mesh may have high aspect ratio or extremely tapered elements that would not be suitable for solution, but can accurately represent the geometry.
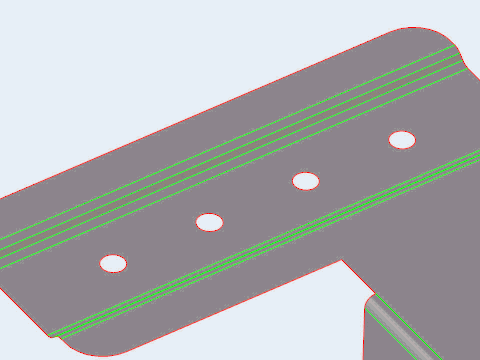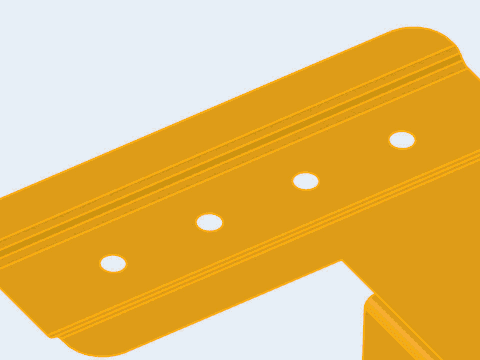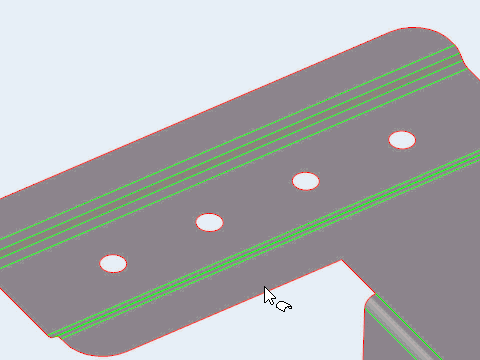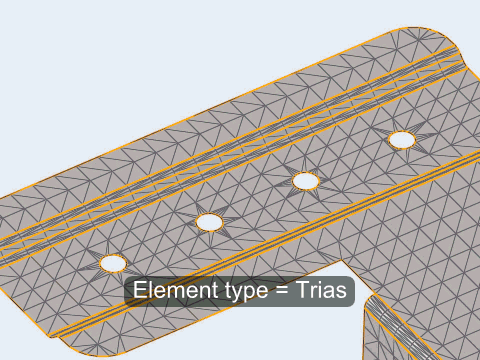
Figure 2.
Rigid Body Mesh Options
- Element size
- Set the average element size.
- Element type
- Select the type of elements used to create the mesh.
- Minimum size factor
- The minimum element size, as a factor of the average element size. Value must be less than or equal to 1.
- Maximum deviation factor
- The maximum allowable deviation between an element edge and a geometry edge, as a factor of the average element size.
- Feature angle
- The maximum allowable break angle between adjacent elements.

 to define surface mesh options.
to define surface mesh options.