Scatter Post Processing
Analyze dependency between two sets of data.
Analyze Dependency Between Two Sets of Data
Analyze the dependency between two sets of data in a scatter plot from the Scatter post processing tab. Visually emphasize data in the scatter plot by appending additional dimensions in the form of bubbles.
- From the Post Processing step, click the Scatter tab.
-
Select data to display in the scatter plot.
- Use the Channel selector to select two dimensions of data to plot.
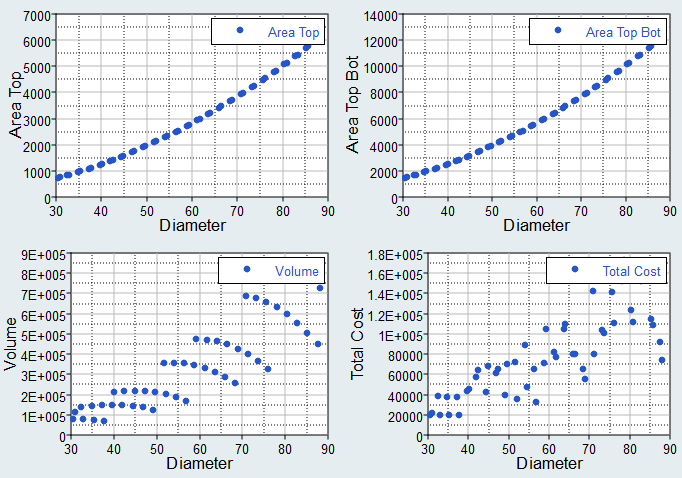
Figure 1. - Use the Correlation selector to select one or
more values from the correlation map to plot.
Correlation measures the strength and direction between associated variables. Correlation coefficients can have a value from -1 to 1; -1 indicates a strong but negative correlation and 1 indicates a strong and positive correlation.
Note: Data points are colored according to their corresponding cell in the correlation map when there are no selections active in the Bubbles selector.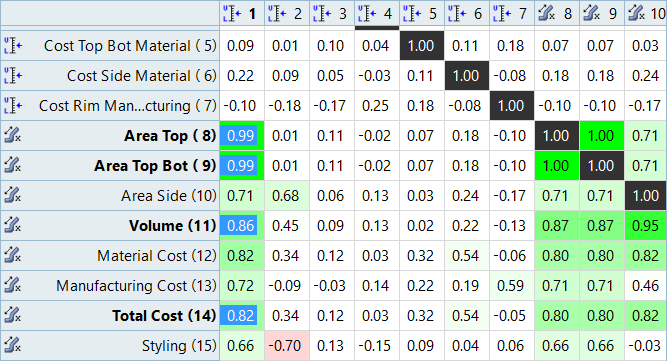
Figure 2. - Use the Bubbles selector to select additional dimensions of data to
visually emphasize in the scatter plot. The selected input variables/output
responses are represented by varying sizes and colors of bubbles.The size and color of bubbles is determined by values in the run data for the selected input variable/output response. For size, larger bubbles equal larger values. For color, different shades of red, blue, and gray are used to visualize the range of values. The darker the shade of red, the larger the value. The lighter the shade of blue, the smaller the value. Gray represents the median value.
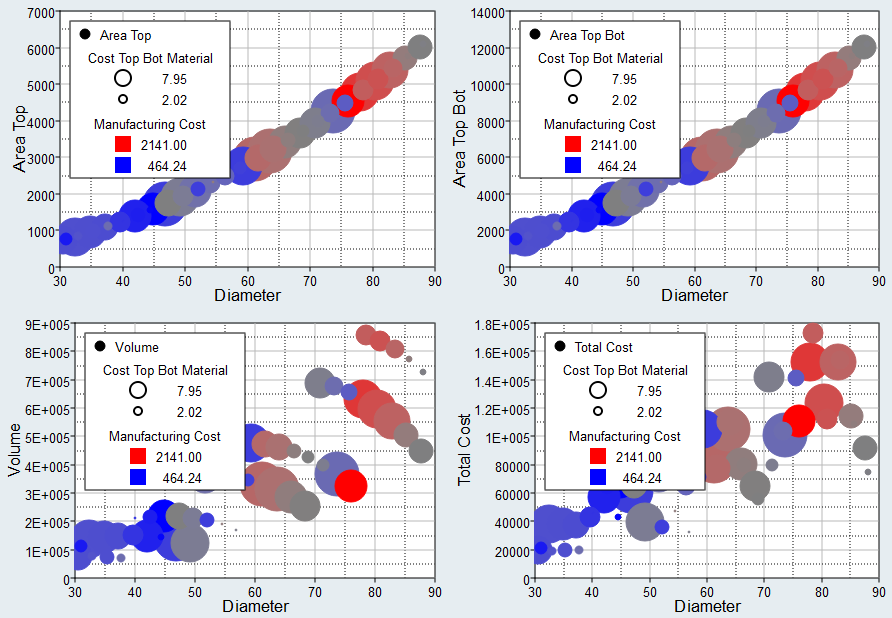
Figure 3.
- Use the Channel selector to select two dimensions of data to plot.
- Analyze the dependencies between the selected data sets.
Scatter Tab Settings
Settings to configure the plots displayed in the Scatter post processing tab.
Access settings from the menu that displays when you click ![]() (located in the top, right corner of the work
area).
(located in the top, right corner of the work
area).
Channel Settings
- X-Bounds
- Display the X bounds in the plot.
- Y-Bounds
- Display the Y bounds in the plot.
Bubble Settings
- Size
- Scale
- Adjust the overall size of all bubbles.
- Focus
- Adjust the size of bubbles so that smaller bubbles become smaller, while larger bubbles remain fixed, enabling the view to be directed at larger bubbles.
- Invert
- Reverse the size of bubbles so that smaller values are represented by larger bubbles.
- Color
- Discrete Steps
- Change the level of color shading applied to bubbles.
- Bins
- Specify the number of red, blue, and gray shades used to color bubbles.
- Invert
- Reverse the color of bubbles so that red represents smaller values and blue represents larger values.