RD-E: 2700 Football (Soccer) Shots
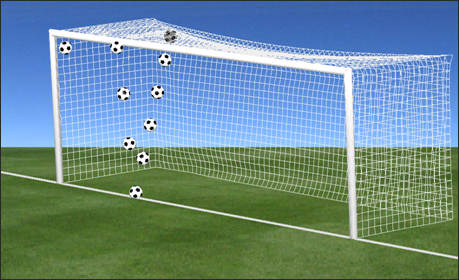
Simulation of a football (soccer) shooting impact on bars.
View new features for Radioss 2019.
Radioss® is a leading explicit finite element solver for crash and impact simulation.
Discover Radioss functionality with interactive tutorials.
This manual provides details on the features, functionality, and simulation methods available in Altair Radioss.
This manual provides a detailed list of all the input keywords and options available in Radioss.
This manual presents examples solved using Radioss with regard to common problem types.
Bending test on a twisted beam modeled with triangular and quadrilateral meshes and different element formulations (QEPH, QBAT, DKT18).
A snap-through problem is studied on a shallow cylindrical roof upon which an imposed velocity is applied at its mid-point. The characteristic curve, caused by the limit load and achieved by simulation is compared to a reference. This example is considered a static problem.
An S-beam is crushed against a rigid wall with initial velocity.
A chambered airbag folded along four fold lines is deployed.
A beam frame receives an impact from a mass having initial velocity.
The fluid-structure interaction and the fluid flow are studied in cases of a fuel tank sloshing and overturning. A bi-phase liquid-gas material with an ALE formulation is used to define the interaction between water and air in the fuel tank.
Five pendulums in line, initially in contact with each other, are struck by a sixth one. The shock wave and oscillating motion are observed.
The high strain rate tensile behavior of the 7010 aluminum alloy is studied using the Hopkinson pressure bar technique (stress wave).
The impact and rebound between balls on a small billiard table is studied. This example deals with the problem of defining interfaces and transmitting momentum between the balls.
Pure bending test with different 3- and 4-nodes shell formulations.
The material characterization of ductile aluminum alloy is studied.
After a quasi-static pre-loading using gravity, a dummy cyclist rides along a plane, then jumps down onto a lower plane. Sensors are used to simulate the scenario in terms of time.
The transitory response of a perfect gas in a long tube separated into two parts using a diaphragm is studied. The problem is well-known as the Riemann problem. The numerical results based on the SPH method and the finite element method with the Lagrangian and Eulerian formulations, are compared to the analytical solution.
This example compares different studies with flexible or rigid bodies. The method for using the flexible bodies in an explicit analysis is also studied.
The problem studied is a twin gear having an identical pitch diameter and straight teeth.
The problem of a dummy positioning on the seat before a crash analysis is the quasi-static loading which can be resolved by either Radioss explicit or Radioss implicit solvers.
The crashing of a box beam against a rigid wall is a typical and famous example of simulation in dynamic transient problems. The purpose for this example is to study the mesh influence on simulation results when several kinds of shell elements are used.
A square plane subjected to in-plane and out-of-plane static loading is a simple element test. It allows you to highlight element formulation for elastic and elasto-plastic cases. The under-integrated quadrilateral shells are compared with the fully-integrated BATOZ shells. The triangles are also studied.
Elastic wave propagation on a half-space subjected to a vertically-distributed load.
Ice cube dropping on two sliding channels.
The modeling of a camshaft, which takes the engine's rotary motion and translates it into linear motion for operating the intake and exhaust valves, is studied.
The ditching of an object into a pool of water is studied using SPH and ALE approaches. The simulation results are compared to the experimental data and to the analytical results.
A brake system is simulated using a finite Lagrangian mesh element.
Two rolling rigid cylinders squeeze a plate to laminate it.
An explicit stamping simulation is followed by a spring-back analysis using implicit or explicit solvers for stress relaxation. Results are compared with a reference.
A metallic thick plate is perforated by a rigid sphere. Simulation of the rupture uses different failure models.
Simulation of a football (soccer) shooting impact on bars.
A cantilever beam submitted to a shear-bending is tested by Radioss linear and nonlinear solvers. Different kinds of Radioss finite elements provide results close to the analytical one.
A Fluid-Structure-Interaction (FSI) problem is studied. The Radioss ALE/CFD solver is used to resolve the problem.
A rubber ring resting on a flat rigid surface is pushed down by a circular roller to produce self-contact on the inside surface of the ring. Then the roller is simultaneously rolled and translated so that crushed ring rolls along the flat surface.
Polynomial EOS is used to model perfect gas. Pressure or energy can be absolute values or relative. Material LAW6 (/MAT/HYDRO) is used to build material cards for each of these cases.
Blow molding with Advanced Mass Scaling (AMS).
Separate the whole model into master domain and sub-domain and solve each one with its own timestep. The new Multi-Domain Single Input Format makes the sub-domain part definition with the /SUBDOMAIN keyword.
The Cylinder Expansion Test is an experimental test used to characterize the adiabatic expansion of detonation products. It allows determining JWL EOS parameters.
The purpose of this example is to compare the simulation results to experimental data. Radioss includes the material model CONC to model concrete failure modeling under compression and tension.
The purpose of this example is to introduce solid element modeling for spotweld connection.
Using SPHCEL to simulate a bird hitting a windshield.
A container that is partially filled with liquid is dropped and the interaction between the liquid and structure can be studied. The liquid fill is defined using /INIVOL and infinite plane /SURF/PLANE. The contact between the structure and liquid is defined using /INTER/TYPE18.
The new feature, Optimization in Radioss, makes it easy to set up an optimization problem in Radioss Block Format.
The purpose of this example is to introduce how to use typical visco-elastic material to simulate creep and stress relaxation tests.
A heat source moved on one plate. Heat exchanged between a heatsource and a plate through contact, also between a plate and theatmosphere (water) through convective flux.
The target of cut methodology is to study one area of the model with taking into account the deformation of the full model through a section force. In the defined section, displacement will be imposed in order to represent the "sub" part of the model. This cut methodology is used to save the computation time. It is often used for component structure study. The aim of this example is to show how to use /SECT to apply this technique.
Impacts of rotating structures usually happen while the structure is rotating at a steady state. When the structure is rotating at very high speeds, it is necessary to include the centrifugal force field acting on the structure to correctly account for the initial stresses in the structure due to rotation.
The target of this example is to demonstrate how to use material test data for rubber hyperplastic materials.
This section provides quick responses to typical and frequently asked questions regarding Radioss.
This manual provides detailed information about the theory used in the Altair Radioss Solver.
The Radioss User Subroutines manual is available in PDF format.
The HyperWorks Solver Run Manager is a unified utility that allows the user to start different HyperWorks Solvers.
This manual presents examples solved using Radioss with regard to common problem types.
Simulation of a football (soccer) shooting impact on bars.
ON THIS PAGE
Simulation of a football (soccer) shooting impact on bars.

ON THIS PAGE
(c) 2019. Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.