OS-E: 0120 Nonlinear Static Analysis with Hyperelastic Material Model, under Compression Loading and Unloading
Behavior of hyperelastic material during loading and unloading phases. Typical examples include rubber mounts, boot seals, and rubber keyboard domes.
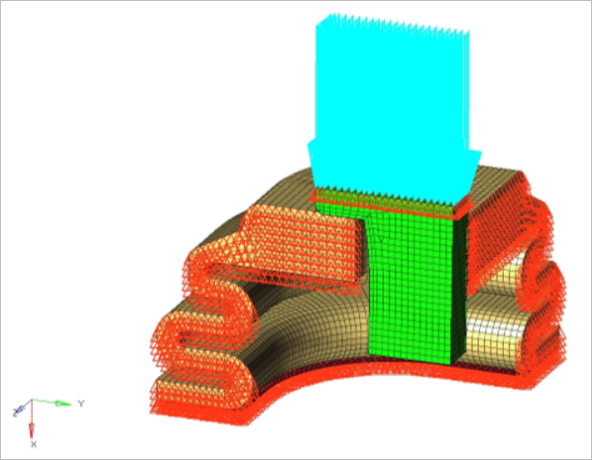
Figure 1. FE Model
Model Description
- FE Model
- Element Types
- CHEXA
- Linear Material
- Young’s Modulus
- 2.1E5 MPA
- Gasket Material
- Poisson Ratio
- 0.3
- Density
- 7.8E-9
- MATHE
- C10
- 400.00
- C01
- 50.0
- D1
- 0.001
Results
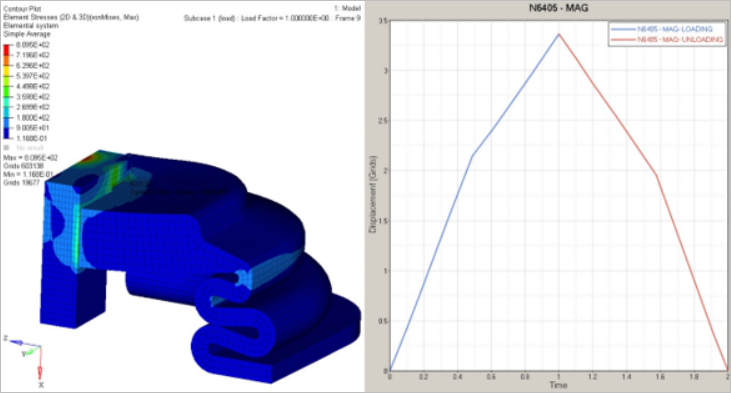 Figure 2. Element Stress Plot and Total Displacement with Loading and
Magnitude
Figure 2. Element Stress Plot and Total Displacement with Loading and
MagnitudeModel Files
The model files used in this example include:
<install_directory>/demos/hwsolvers/optistruct/examples/HYPERELASTIC.fem