AutoReboundStop
The AutoReboundStop entity limits the movement of the suspension while in rebound or extension by applying a line of sight force between two components when their distance exceeds a specified value.
$(ALTAIR_HOME)\hw\mdl\autoentities\properties\Bumpers-Rebound
AutoReboundStop Force
- Elastic force or stiffness
- Viscous force or damping
For a linear AutoReboundStop, the elastic force component is calculated using a third order polynomial and for a non-linear AutoReboundStop, the elastic force component is interpolated using the Akima method.
The viscous force component is optional and when defined in the property file, is calculated directly from the damping rate in the property file and resultant instantaneous velocity between the two bodies.
Install Methods
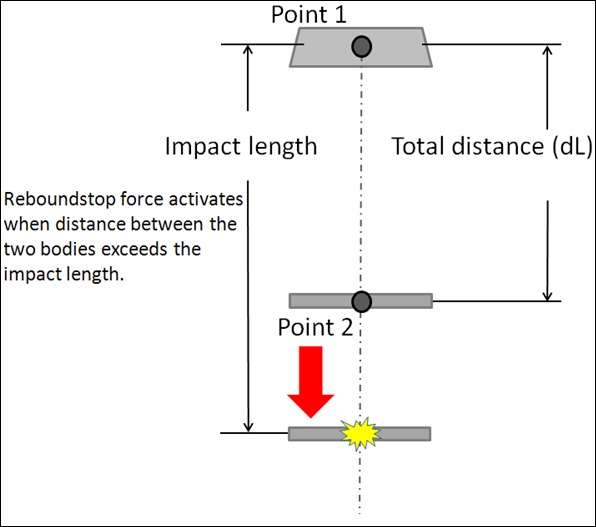
The AutoReboundStop install method is at design position and is used to determine the distance at which the AutoReboundStop force starts acting.
- Impact Length Method
- When the impact length is of value ‘L’, the AutoReboundStop force acts when the distance between the two bodies is less than ‘L’.
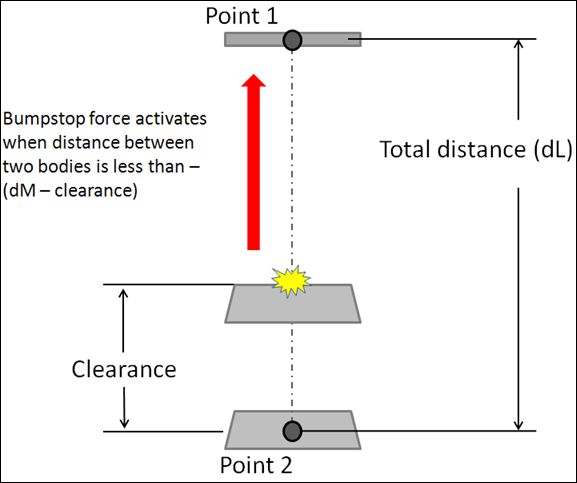
- Clearance Method
- When the Clearance method is used, the impact distance is calculated
using:
(1)
Connecting an AutoReboundStop
Connections define the two bodies between which the ReboundStop force acts and select two points that are used to calculate the impact distance. The ReboundStop force acts between Body 1 and Body 2. The initial distance is measured between Point 1 and Point 2.
The ReboundStop force is activated when the distance between the two bodies exceeds a certain value. The distance at which the ReboundStop force starts acting is calculated based on the installation method.
-
From the Connectivity tab, select the first body to
connect.
- Click Body 1 and select a body from the modeling window.
- Double click Body 1 and select the required body from the dialog.
- Similarly, select the second body to connect by clicking the Body 2 input collector.
- Select the first point.
- Similarly, select the second point.
- Optional: Check the Output box to add an output request for the ReboundStop resultant displacement, resultant velocity, and resultant force. These outputs are measured between I and J markers.
AutoReboundStop Output Channels
Activating the Output check box adds an output request for the AutoReboundStop resultant displacement, resultant velocity, and resultant force. These outputs are measured between I and J markers.
| Type | Component | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| REQSUB | RESULT(2) | Distance between I and J markers of the ReboundStop. |
| RESULT(3) | Rate-of-change-of-displacement between I and J markers. | |
| RESULT(4) | ReboundStop force. | |
| RESULT(6) | Global X direction cosine of ReboundStop. | |
| RESULT(7) | Global Y direction cosine of ReboundStop. | |
| RESULT(8) | Global Z direction cosine of ReboundStop. |
AutoReboundStop Properties File
The AutoReboundStop properties are stored in a TeimOrbit File Format text file. When you resolve the property file field to a AutoReboundStop property file and submit the model to the solver, the solver reads the AutoReboundStop property file for use during simulation. If the units in the property file differ from the model units, the solver internally converts the AutoReboundStop properties to the model units. The properties file remains unchanged.
The AutoReboundStop properties file contains header, units, and curve blocks. The units block specifies the length, mass, force, time, and angle units employed in the file. The curve block holds a table of displacement against force values for the elastic force component and optionally a velocity against force values for the viscous force component.
$--------------------------------------------------------------------HEADER
[HEADER]
FILE_TYPE = 'reb'
FILE_VERSION = 4.0
FILE_FORMAT = 'ASCII'$
---------------------------------------------------------------------UNITS
[UNITS]
LENGTH = 'mm'
ANGLE = 'degrees'
FORCE = 'newton'
MASS = 'kg'
TIME = 'second'
$---------------------------------------------------------------------CURVE
[CURVE]
{ disp force}
0.0 0.0
2.0 1.0
4.0 2.0
6.0 3.0
8.0 4.0
10.0 5.0
20.0 6.0
30.0 7.0
40.0 8.0
50.0 9.0