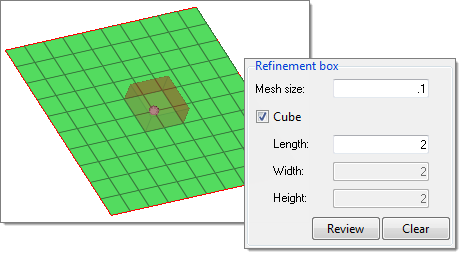
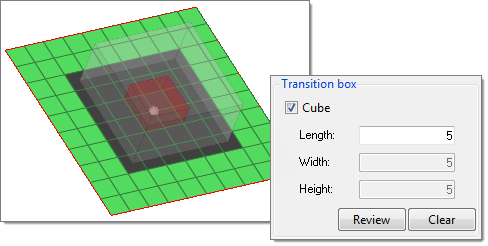
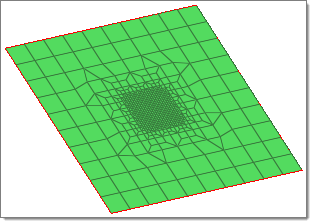
Refine Mesh by Pattern
Create a regular orthogonal mesh.
Before you begin, make sure the initial mesh is a regular mapped quad mesh, and not a free quad mesh.
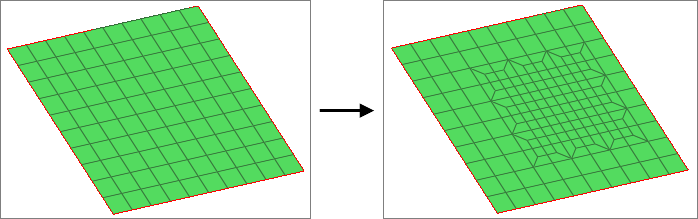
Figure 1. Pattern Based Mesh Refinement
View new features for HyperMesh 2019.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperMesh functionality with interactive tutorials.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperMesh.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Support provided by the CAD readers and writers.
Browsers supply a great deal of view-related functionality in HyperMesh by listing the parts of a model in a tabular and/or tree-based format, and providing controls inside the table that allow you to alter the display of model parts.
Pre-processing and post-processing tools are displayed on panels located at the bottom of the application.
Create and edit geometry.
Learn about the different types of mesh you can create in HyperMesh.
Elements are FE idealizations for a portion of a physical part.
Configure criteria and parameter settings.
Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), Finite Point Method (FPM) is a technique used to analyze bodies that do not have high cohesive forces among themselves and undergo large deformation, such as liquids and gases.
1D mesh that allows accurate testing of connectors, such as bolts, and similar rod-like or bar-like objects that can be modeled as a simple line for FEA purposes.
A surface mesh or "shell mesh" represents model parts that are relatively two-dimensional, such as sheet metal or a hollow plastic cowl or case.
Volume mesh or "solid meshing" uses three-dimensional elements to represent fully 3D objects, such as solid parts or sheets of material that have enough thickness and surface variety that solid meshing makes more sense than 2D shell meshing.
Mesh controls are used to automate and streamline the meshing process.
Evaluate the overall quality of a mesh, and resolve criteria violations.
Modify your mesh by detect holes, locating edges or features, refining mesh pattern, and so on.
Locate holes in a model, and potentially all of them, define them, and add them as geometry to a new component or to the current one.
Create a regular orthogonal mesh.
Scale the thickness of elements in your model.
Calculate and assign the thickness of a midmesh from solid geometry using the Midmesh Thickness tool.
Simplify a mesh by combining many small elements into a smaller number of larger ones.
Connect intersecting triangular and quadrilaaterial 2D elements.
Connect close proximity, overlapping and intersecting parts.
Fill holes, gaps, and patches in first order and second order elements.
Batchmesher is a tool that performs geometry feature recognition, cleanup and automatic meshing in batch mode for given CAD files.
Create connections between parts of your model.
Create, organize, and manage the CAE parts.
Perform automatic checks on CAD models, and identify potential issues with geometry that may slow down the meshing process using the Verification and Comparison tools.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Overview of how to build a finite element model.
Morph the shape of your finite element model.
Setup an Optimization in HyperMesh.
Convert finite element models to another solver format.
Study relationships between data vectors in results files.
Learn how to use post-processing functions.
Learn about the different types of mesh you can create in HyperMesh.
Modify your mesh by detect holes, locating edges or features, refining mesh pattern, and so on.
Create a regular orthogonal mesh.
Create a regular orthogonal mesh.
Before you begin, make sure the initial mesh is a regular mapped quad mesh, and not a free quad mesh.

(c) 2019. Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.