Tied Interface (TYPE2)
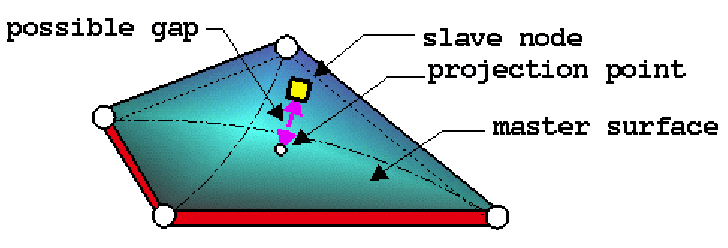
A master and a slave surface are defined in the interface input cards. The contact between the two surfaces is tied. No sliding or movement of the slave nodes is allowed on the master surface. There are no voids present either.
It is recommended that the master surface has a coarser mesh.
Accelerations and velocities of the master nodes are computed with forces and masses added from the slave nodes.
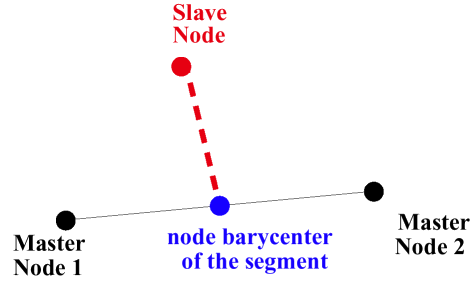
Kinematic constraint is applied on all slave nodes. They remain at the same position on their master segments.
Tied interfaces are useful in rivet modeling, where they are used to connect springs to a shell or solid mesh.
Spotweld Formulation
- Default formulation
- Optimized formulation
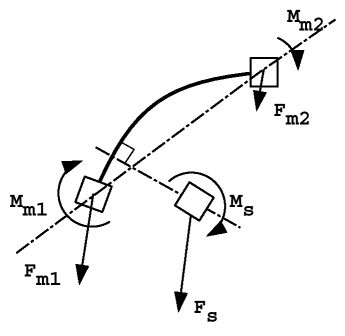
Default Spotweld Formulation
- Based on element shape functions
- Generating hourglass with under integrated elements
- Providing a connection stiffness function of slave node localization
- Recommended with full integrated shells (master)
- Recommended for connecting brick slave nodes to brick master segments (mesh transition without rotational freedom)
- p
- Denotes the position of the slave point
- Φ
- Weight function obtained by the interpolation equations
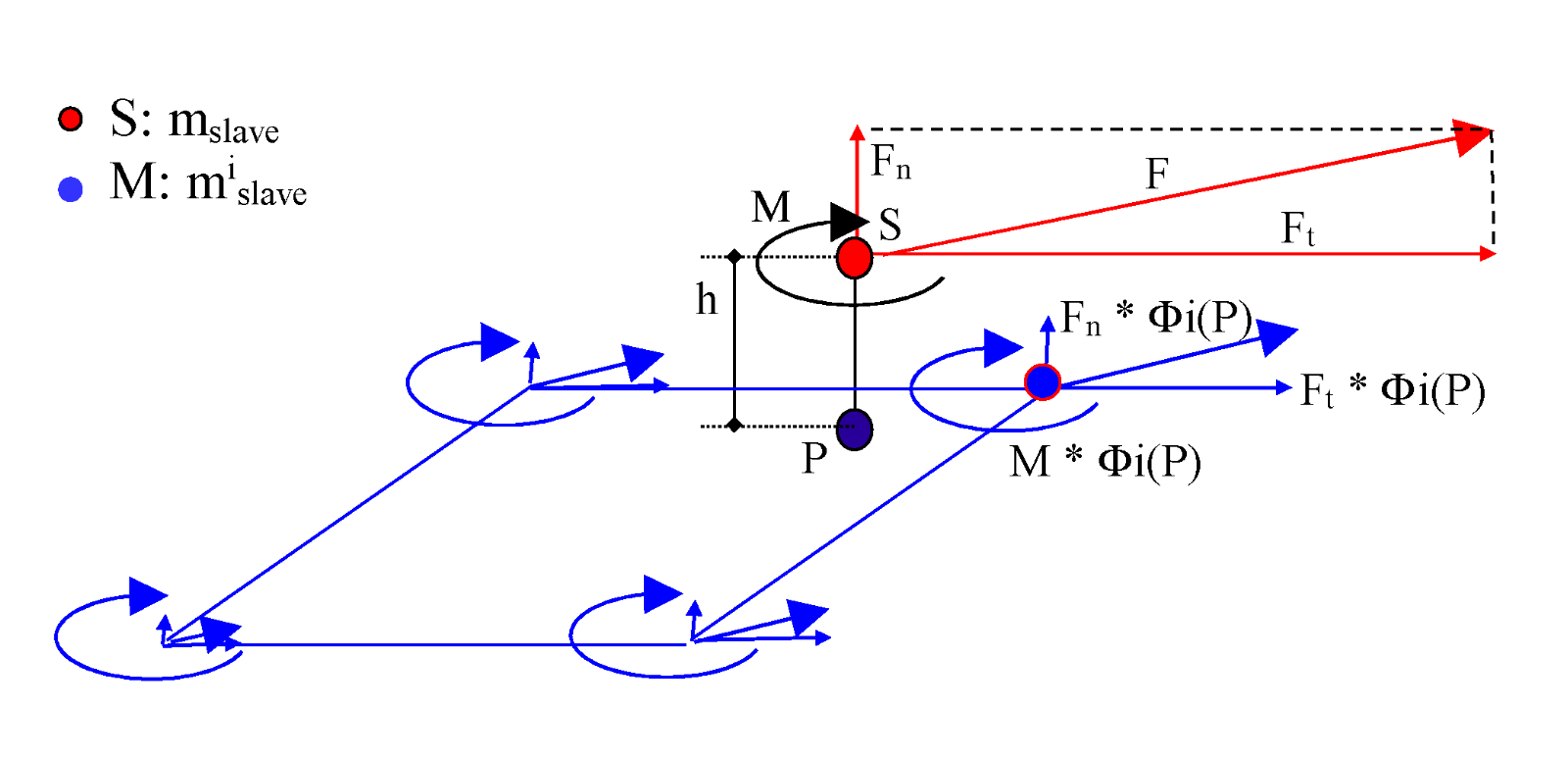
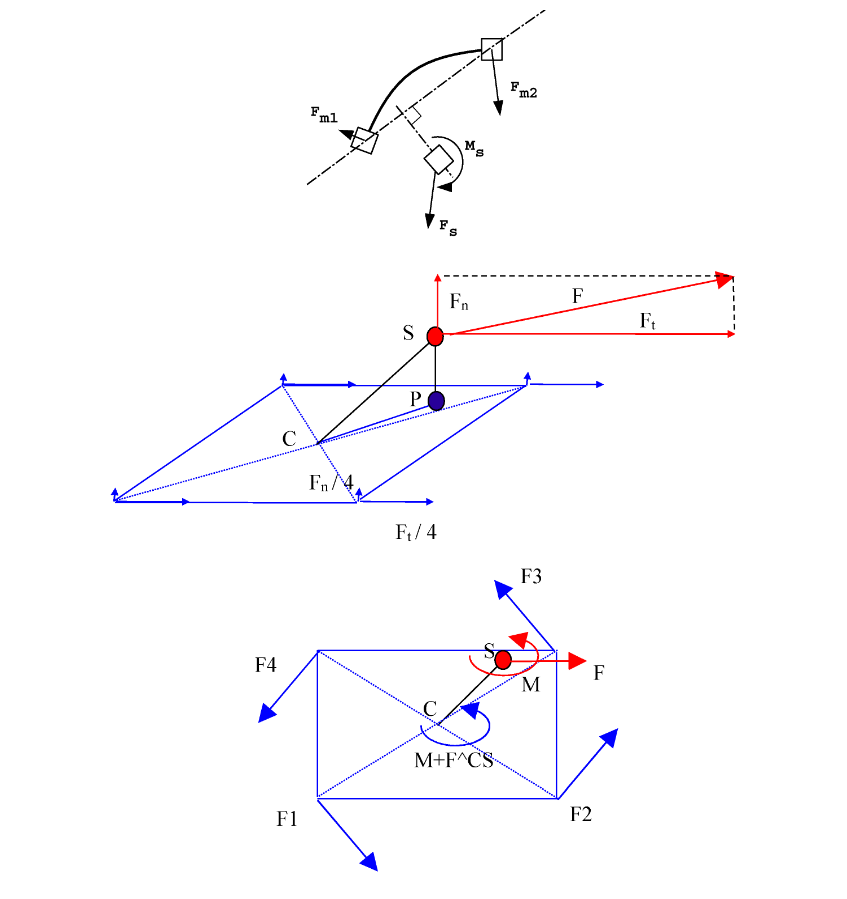
The term mslave∗d2 may increase the total inertia of the model especially when the slave node is far from the master surface.
With this formulation, the added inertia may be very large especially when the slave node is far from the mean plan of the master element.
Optimized Spotweld Formulation
- Based on element mean rigid motion (i.e. without exciting deformation modes)
- Having no hourglass problem
- Having constant connection stiffness
- Recommended with under integrated shells (master)
- Recommended for connecting beam, spring and shell slave nodes to brick master segments
This spotweld formulation is optimized for spotwelds or rivets.
- →A
- Normal vector to the segment
Closest Master Segment Formulation
- Old formulation
- New improved formulation
Old Search of Closest Master Segment Formulation
When Isearch= 1, the search of closest master segment was based on the old formulation.
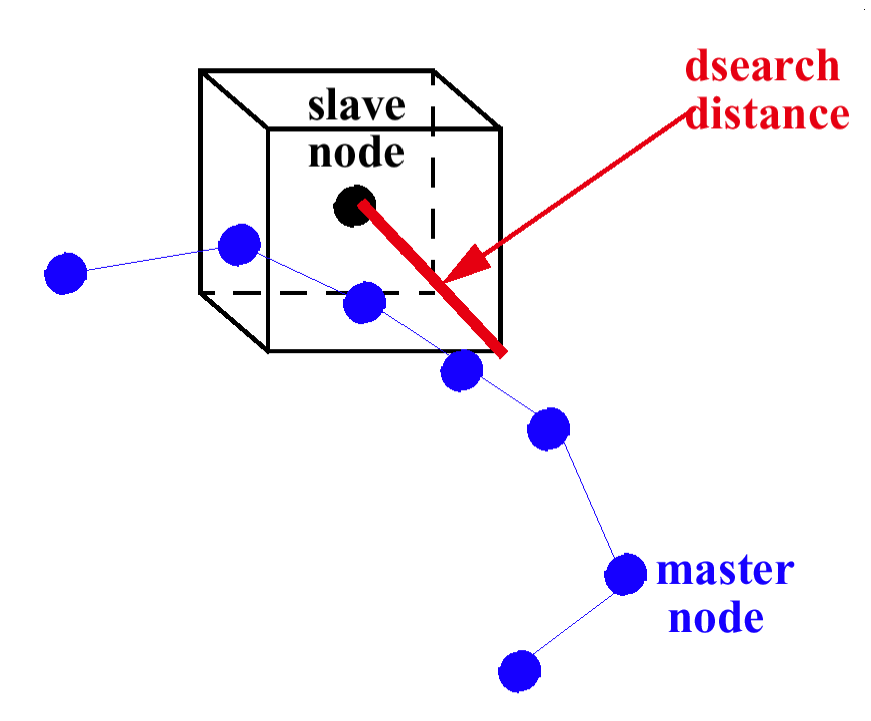
The distance between each master node in the box and the slave node is computed.
The master node giving the minimum distance (dmin) is retained.
New Improved Search of Closest Master Segment Formulation
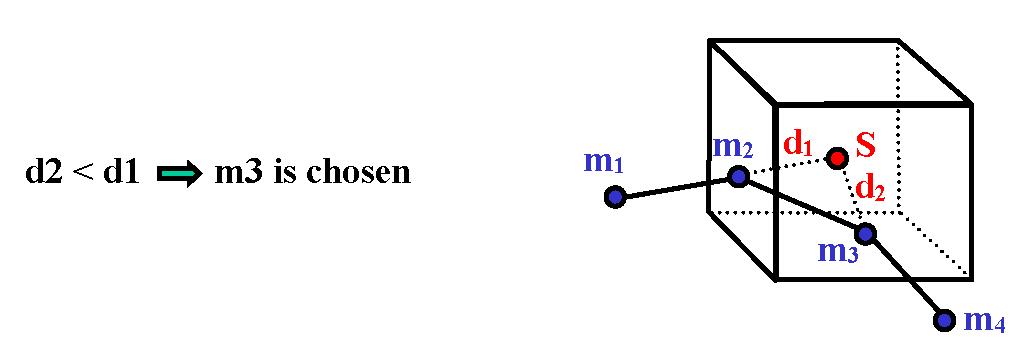
When Isearch=2, the search of closest master segment is based on the new improved formulation; a box including the master surface is built.
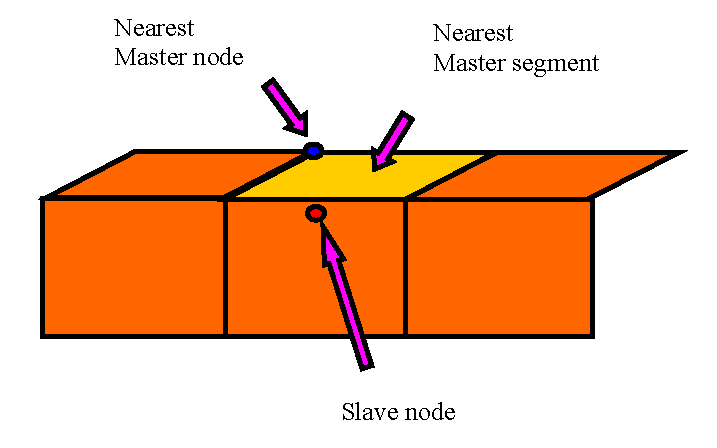
- The slave node is an internal node for the master segment, as shown in Figure 10.The slave node is projected orthogonally on the master segment to give a distance that may be compared with other distances. Select the minimum distance:Figure 10. Orthogonal Projection on the Master Segment
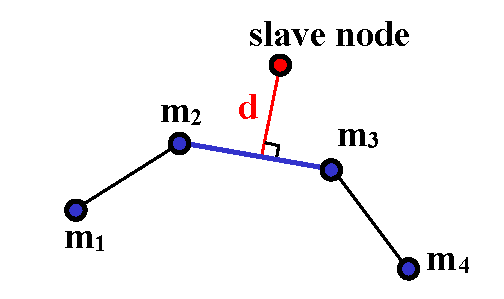
The segment that provides the minimum distance is chosen for the following computation.
- The slave node is a node external to the master segment, as shown in Figure 11.The distance selected is that between the slave node and the nearest master node.Figure 11. Nearest Master Node
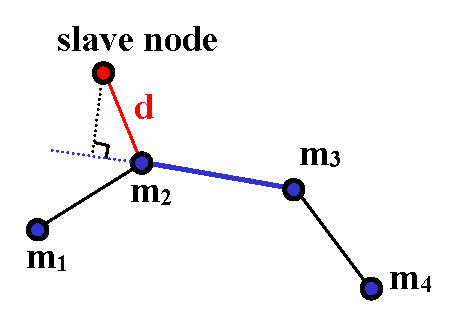
The segment is chosen using the selected node, (if the selected node belongs to 2 segments, one is chosen at random).