Ityp = 3
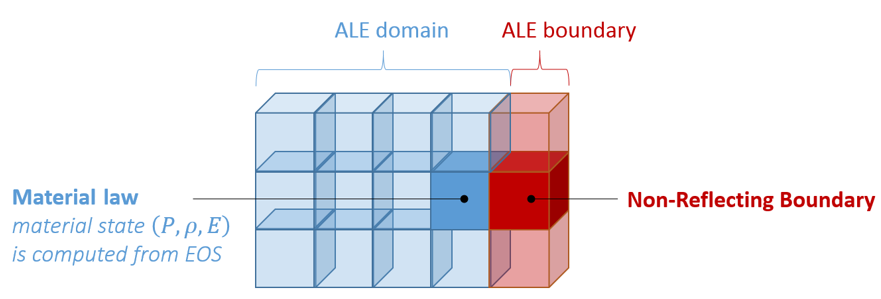
This law enables to model a non-reflecting boundary (NRF).
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /MAT/LAW11/mat_ID or /MAT/BOUND/mat_ID | |||||||||
| mat_title | |||||||||
| ρi | ρ0 | ||||||||
| Ityp | Psh | ||||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c | lc | ||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| mat_ID | Material identifier (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| mat_title | Material title (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| ρi | Initial density 3 (Real) |
[kgm3] |
| ρ0 | Reference density used in E.O.S
(equation of state) Default ρ0=ρi (Real) |
[kgm3] |
| Ityp | Boundary condition type 1
(Integer) |
|
| Psh | Pressure shift 2 (Real) |
[Pa] |
| c | Outlet sound speed 1 (Real) |
[ms] |
| lc | Characteristic length 1 (Real) |
[m3] |
Comments
- Non-Reflecting Boundary formulation is
based on Bayliss & Turkel. 1 The objective is to impose a mean pressure which fluctuate with
rapid variations of pressure and velocity:
(1) ∂P∂t=ρc(∂∂t(Vn)−Vn⋅div(→V−Vn⋅→n))+c(P∞−P)2lcPressure in the far field P∞ is imposed with a function of time. The transient pressure is derived from P∞ , the local velocity field V and the normal of the outlet facet:- density, energy, temperature, turbulent energy and dissipation are imposed with a function of time as in Ityp = 2
- if the function number is 0, the neighbor element value is used to respect continuity
- acoustic impedance will be ρc
- typical length
lc
is used to relax the effective pressure towards its
imposed value. It should be large compared to the highest wave length of interest in
the problem. The relaxation term acts as high pass filter whose frequency cut-off
is:
(2) fc=c4⋅π⋅lcWhere, sound speed c and characteristic length lc are two required parameters (non zero).
- The Psh parameter enables shifting the output pressure which also becomes P-Psh. If using Psh=P(t=0), the output pressure will be ΔP , with an initial value of 0.0.
- With thermal modeling, all thermal data ( T0, ρ0CP , ...) can be defined with /HEAT/MAT.
- It is not possible to use this boundary material law with multi-material ALE laws 37 (/MAT/LAW37 (BIPHAS)) and 51 (/MAT/LAW51 (MULTIMAT)).