Data Types
The mathematical functions accept arguments of different data types.
Constants
PI is the only predefined constant within the math engine. All other constants are user-defined. Constants are case sensitive.
Matrices
A matrix is a two-dimensional array. It is a collection of vectors containing the
same number of elements. The dimensions of a matrix are described as m x
n, pronounced "m by n". m refers to the number of rows
(values read horizontally) and n refers to the number of columns
(values read vertically).
{ {1, 2, 3, 5}, {-1, -1, -2, -3} }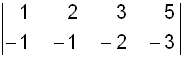
Figure 1.
In the previous example it could be said the matrix has two row vectors of four elements, or four column vectors of two elements.
If the matrix has the same number of rows as columns, the matrix is a square matrix. There are some functions that require a square matrix.
Scalars
Scalars are numbers that denote a magnitude without direction. Examples of a scalar value are 11, -4.5, and the value of PI.
Strings & String Arrays
"This is a test"{"This", "is", "a", "test"}Addition, +, and equality, ==, are the only mathematical operations that can be performed on a string or string array. Concatenation performs a similar, but not identical, operation.
Vectors
{2, 4}
{3, -16, 8.5}
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
1:5:1